Modern Web Development: A quick inspection

Table of Contents
- Modern Web Development: Understanding Workflow and Core Components
- Contemporary Web Development Workflow
- 1. Local Devices: Starting the Development Process
- 2. Git for Tracking Code Changes
- 3. CI/CD Tools for Automation
- 4. Hosting and Deployment
- 5. File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- 6. Web Browsers: The Final Access Point
- Core Components of Modern Web Development
- Conclusion
Modern Web Development: Understanding Workflow and Core Components
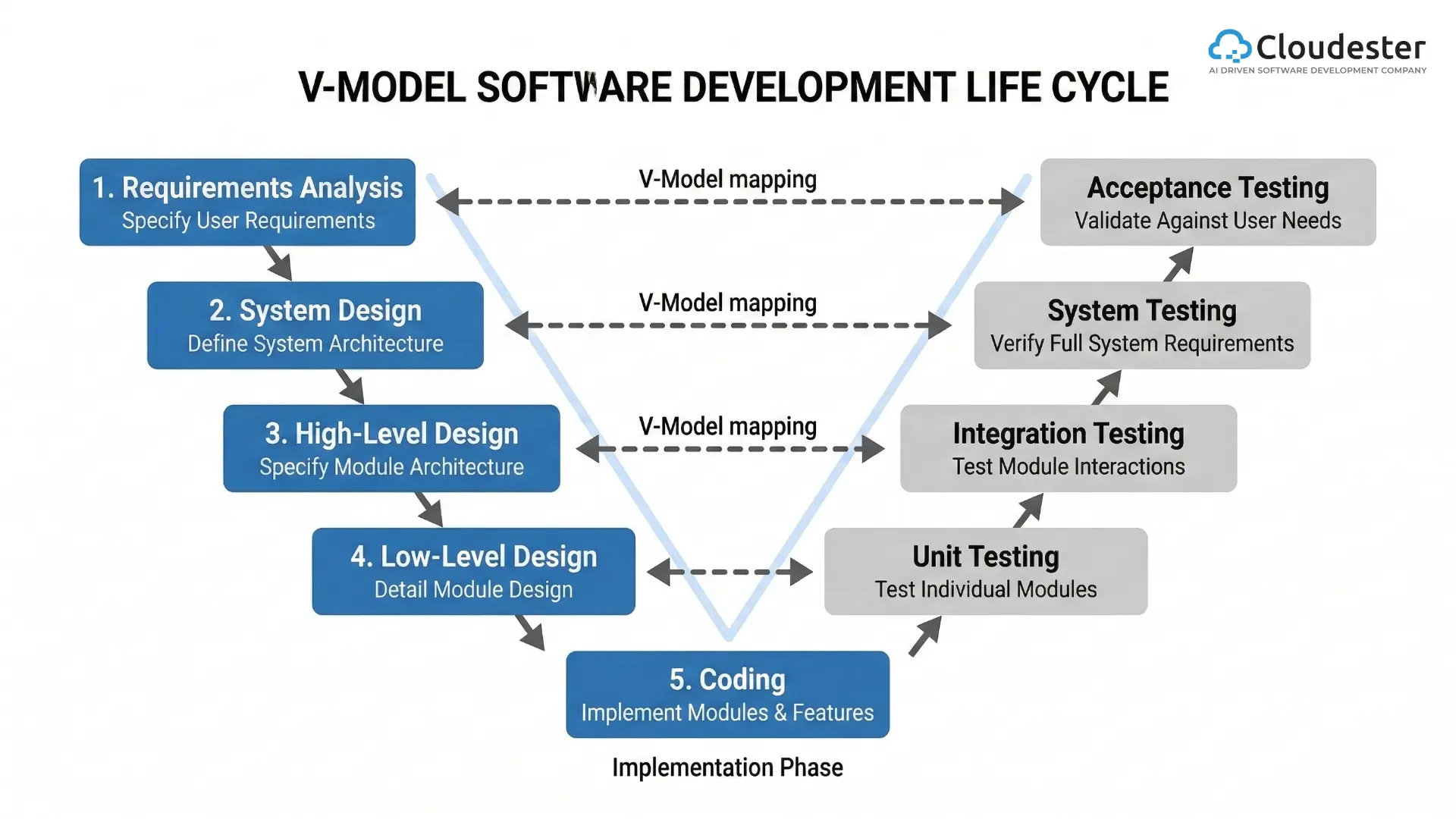
Since the rise of the internet as a commercial tool, web development has evolved dramatically. Today, it combines innovation, design, and functionality to deliver seamless digital experiences. While some developers embrace modern web development, others find it complex and challenging. However, understanding its workflow and core components helps anyone appreciate how this process works.
Contemporary Web Development Workflow
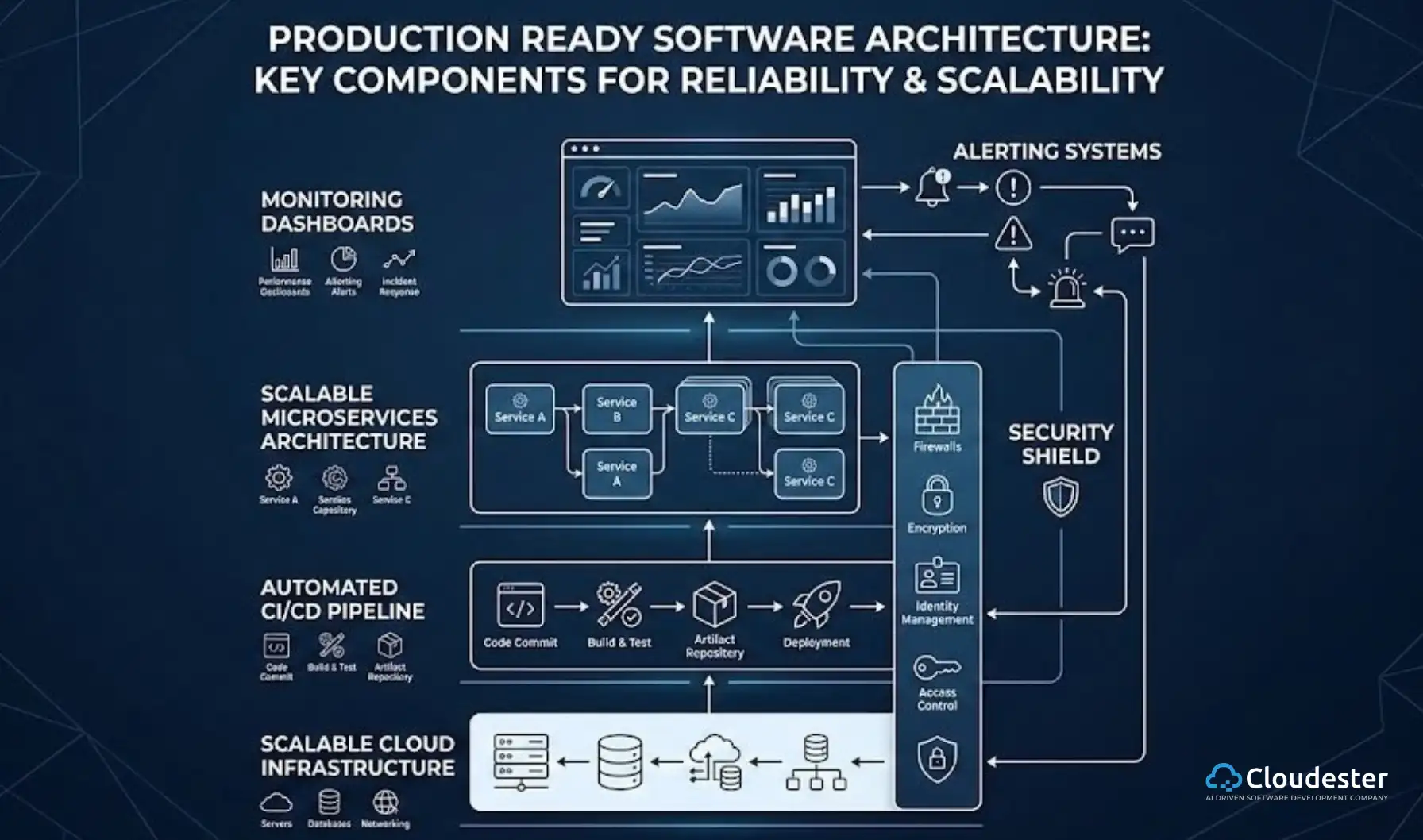
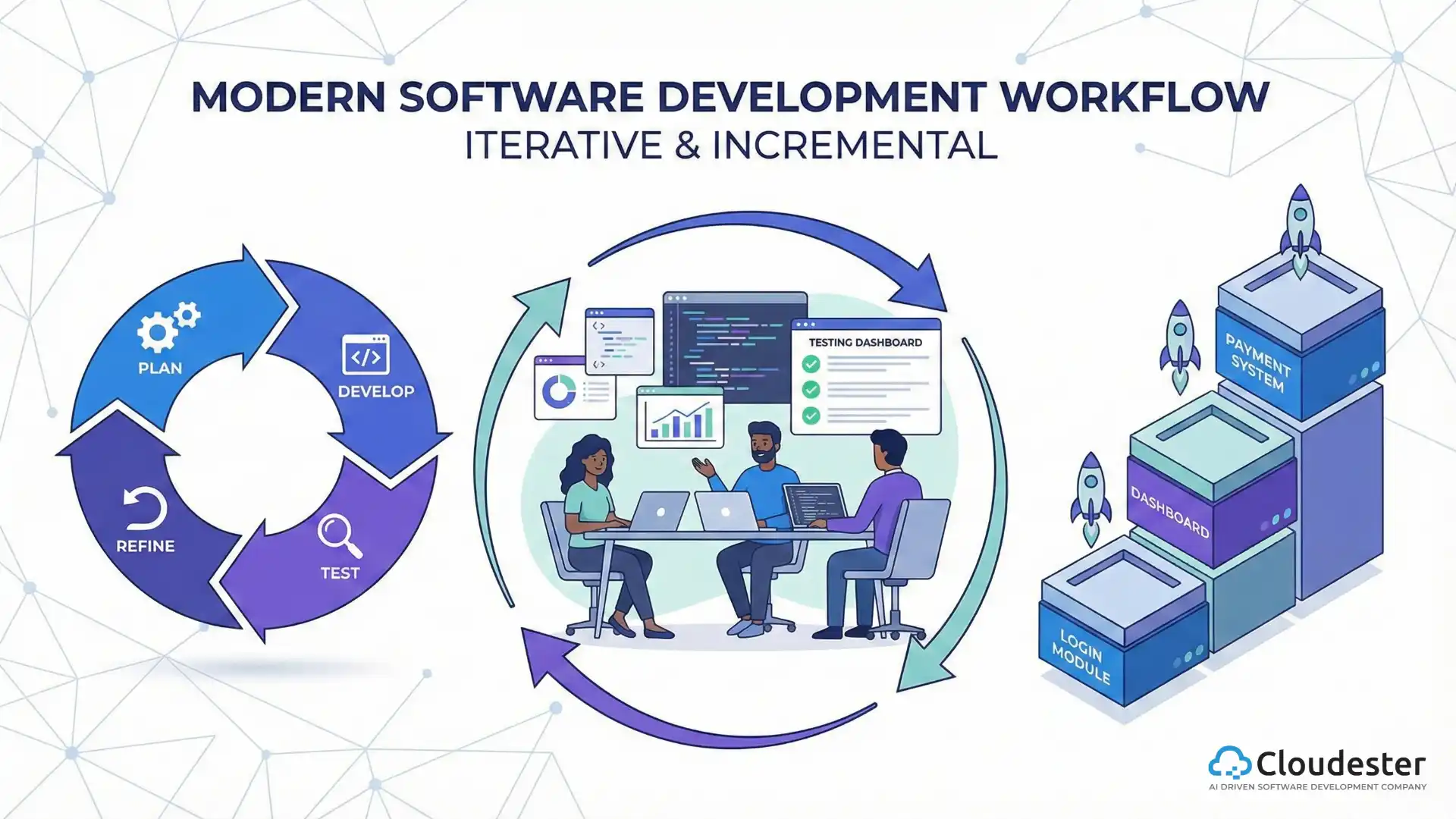
Modern web development relies on collaboration, automation, and cloud connectivity. Developers now use structured workflows to ensure faster delivery and better code quality.
1. Local Devices: Starting the Development Process
Web developers begin by writing code on their local computers. This code is typically divided into two parts , backend and frontend.
Backend: Handles server-side logic using languages like Python, Java, .NET, PHP, and Node.js.
Frontend: Manages user-facing elements built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Together, these components power dynamic web applications that run smoothly in the browser.
2. Git for Tracking Code Changes
Developers use Git, a version control system, to manage and track changes in their code. Git repositories are stored locally and synchronized with cloud services like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
This system helps developers maintain project versions, collaborate efficiently, and access updated code from anywhere. Moreover, storing code in the cloud simplifies deployment and enhances team coordination.
3. CI/CD Tools for Automation
Once the code is pushed to the cloud, Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) tools come into play. These tools automatically test, build, and deploy the application, ensuring that the latest updates reach the hosting environment without manual intervention.
Popular CI/CD tools include Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI/CD, which help developers streamline delivery and maintain code quality.
4. Hosting and Deployment
After CI/CD deployment, the application is hosted on cloud servers. Once connected to a registered domain, users can access the site through their web browsers. Hosting options include platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, depending on scalability and performance requirements.
5. File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Some developers still use File Transfer Protocol (FTP) to upload code to online servers. However, this method is now outdated and less secure. Modern CI/CD pipelines offer safer and more automated alternatives for code deployment.
6. Web Browsers: The Final Access Point
Once hosted, the website or web app becomes publicly accessible. When a user visits the domain, the frontend loads in the browser, and any user interaction triggers backend scripts on the server. These scripts process the request and send data back to display dynamic content.
Core Components of Modern Web Development
Modern web development combines powerful tools and frameworks that balance complexity, performance, and simplicity. Here are two critical technologies driving today’s web landscape:
- React.js – Developed by Meta, React.js remains one of the most popular tools for building modern web applications. It enhances scalability and efficiency, allowing developers to create dynamic and responsive user interfaces with reusable components.
- Web Components – Web components provide developers with the ability to create reusable custom elements. These elements simplify development and include three main technologies: HTML Templates, Shadow DOM, and Custom Elements. Together, they improve code organization and reduce complexity in large projects.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
Conclusion
Modern web development is an ever-evolving field shaped by emerging technologies and user demands. With smartphones and cloud computing transforming how websites operate, developers must constantly adapt to new tools and practices.
While building modern web applications requires effort and skill, the process has become more efficient and creative than ever. Businesses looking to build or upgrade their online presence should always work with experienced developers who understand performance, scalability, and user experience.
In essence, modern web development is not just about coding; it is about crafting seamless digital experiences that connect technology with people.