The Stages of the Agile Software Development Life Cycle
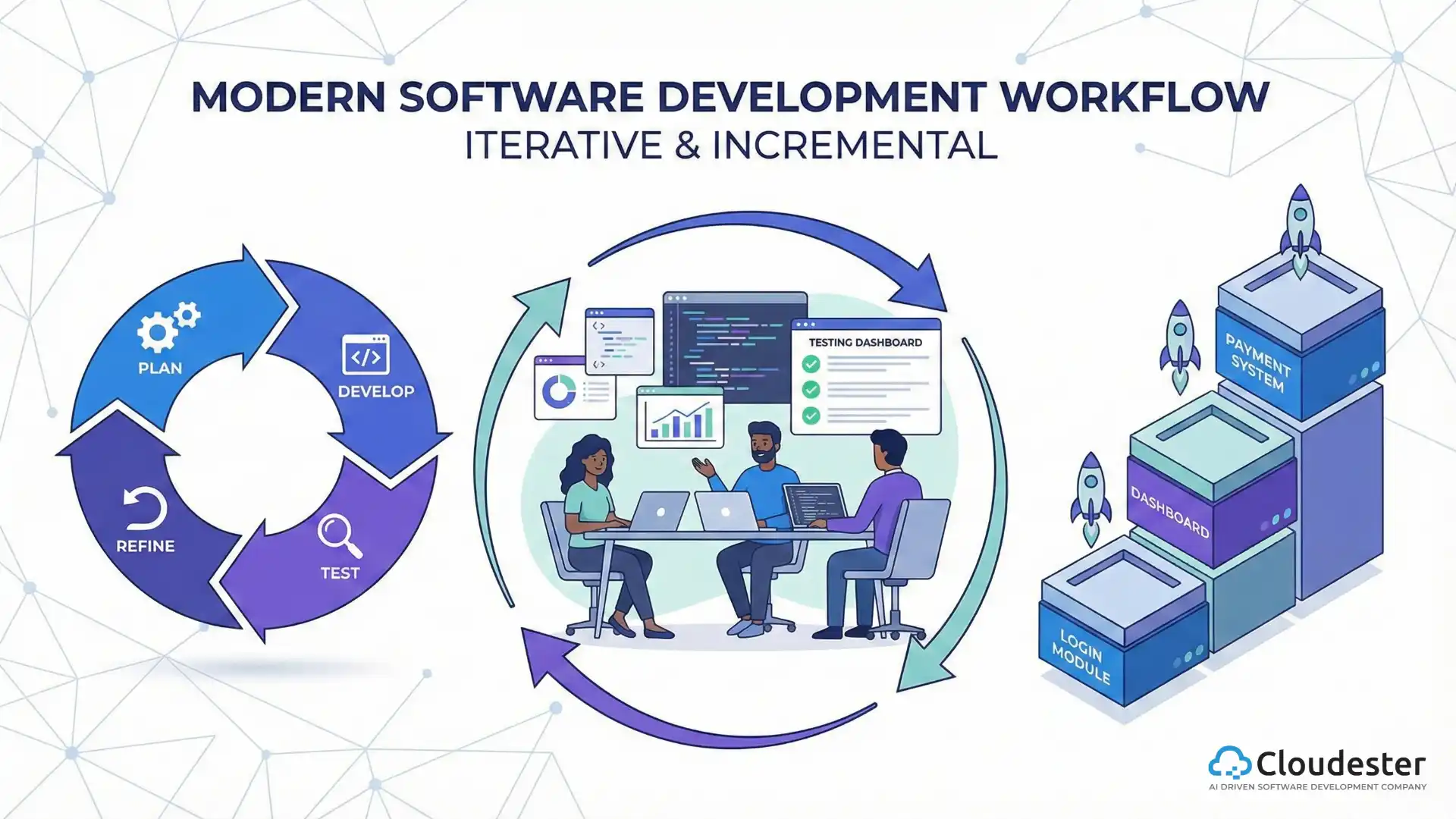
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle explains how teams plan, build, test, and release software in small, repeatable steps. Instead of following one long fixed process, Agile breaks work into short cycles so teams can adapt to changes and deliver results faster.
This approach focuses on collaboration, user feedback, and steady improvement. After each cycle, teams review progress, adjust priorities, and prepare for the next phase. This creates better transparency, fewer delays, and more predictable outcomes.
Agile works for startups, growing companies, and large enterprises because it can be shaped around different project sizes and goals.
What Is the Agile Software Development Life Cycle
The Agile life cycle is a structured process that divides software development into short work cycles, often called sprints. Each cycle includes planning, design, development, testing, and review.
This allows teams to:
- Deliver working features frequently
- Adjust to feedback quickly
- Reduce risks during development
- Keep stakeholders informed throughout the project
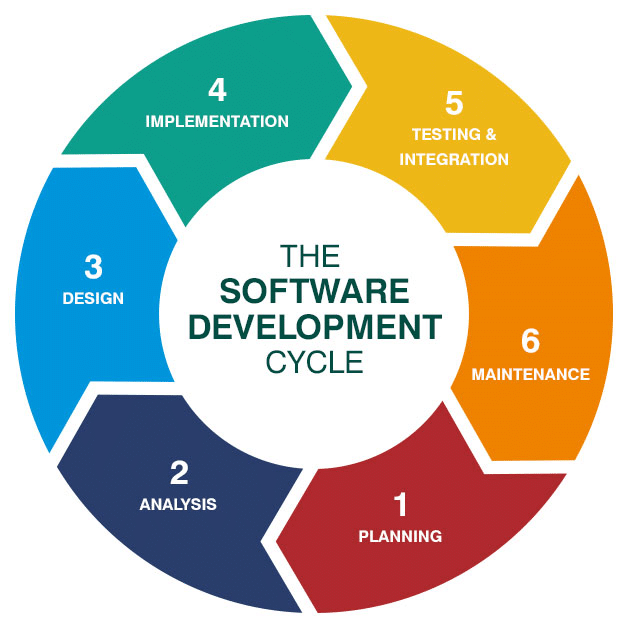
The 6 Key Stages of the Agile Software Development Life Cycle
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
Stage 1: Planning
In the planning stage, teams meet with stakeholders to understand business goals and user needs. They define the product vision, outline the initial scope, and create a high level roadmap.
Clear planning helps:
- Align the team with project goals
- Prevent unnecessary scope changes
- Set realistic expectations
Stage 2: Analysis
During analysis, requirements are turned into simple, clear user stories. These are added to a prioritized task list, often called a backlog.
The team:
- Estimates effort for each task
- Assigns responsibilities
- Sets goals for the next sprint
Most Agile sprints run for one to two weeks to keep work focused and predictable.
Stage 3: Design
In the design stage, developers and designers work together to define user flows, wireframes, and technical approaches.
Design remains flexible so teams can:
- Adjust features based on feedback
- Improve usability
- Ensure the product matches real user needs
Stage 4: Implementation
During implementation, developers write code in small, manageable pieces. They integrate and test changes regularly to detect issues early.
Key practices in this stage include:
- Daily team check ins
- Version control for code changes
- Continuous integration of new features
This keeps development organized and reduces the risk of major issues later.
Stage 5: Testing and Integration
Testing happens throughout the sprint, not just at the end. Teams perform:
- Unit tests for individual features
- Integration tests to check system behavior
- User testing for real world feedback
Quality assurance specialists work alongside developers to identify and fix issues quickly.
Stage 6: Maintenance
After testing, the team releases the updated version through an automated build and deployment process.
In this stage, teams:
- Demonstrate new features
- Collect user feedback
- Log improvements for the next sprint
This continuous feedback loop helps the product evolve over time.
Continuous Feedback in Agile Development
Feedback is central to Agile. At the end of each sprint, teams hold review meetings to show progress and gather input. They also run internal retrospectives to discuss what worked well and what should change.
This process helps:
- Improve team performance
- Align development with user needs
- Reduce long term technical risks
Each sprint builds on the previous one, creating steady and measurable progress.
Benefits of the Agile Software Development Life Cycle
Following the Agile process provides several advantages:
- Faster delivery of new features
- Better communication between teams
- Improved product quality
- Early detection of issues
- Higher customer satisfaction
Because work is delivered in small increments, teams can respond quickly to changing requirements.
Also read: Software Development Phases Guide – A Detailed Overview
When to Use the Agile Approach
Agile works best when:
- Requirements may change over time
- Fast delivery is important
- Teams need regular feedback
- Products must evolve after launch
It is commonly used for:
- Startup MVPs
- SaaS platforms
- Enterprise software
- Mobile and web applications
Conclusion:
The Agile Software Development Life Cycle divides software development into six clear stages: planning, analysis, design, implementation, testing, and maintenance. By working in short cycles and using continuous feedback, teams can stay flexible and deliver consistent value.
Agile helps organizations move faster, reduce risks, and build software that meets real user needs.
FAQ: Agile Software Development Life Cycle
- What is the Agile software development life cycle
- It is a process where software is built in short, repeatable cycles with regular feedback and improvements.
- How long is an Agile sprint
- Most sprints last one to two weeks, depending on the team and project goals.
- Why is Agile better than traditional methods
- Agile allows teams to adapt to changes, deliver features faster, and reduce risks through continuous testing and feedback.
- Who should use Agile development
- Startups, SMBs, and enterprises building software products or internal systems can all benefit from Agile methods.