Transforming Healthcare: How Software and AI Are Shaping its Future

Image credit: canva.com
Imagine a healthcare system where potential illnesses are detected before symptoms appear, where consulting a doctor can happen via video call from home, and where your medical history moves securely and effortlessly between different healthcare providers. This marks a strong healthcare transformation; it’s becoming reality thanks to advancements in software development and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Let’s explore how these technologies work together to make healthcare more efficient, reliable, and personalized.
Why Technology is Crucial in Healthcare IT
Healthcare Information Technology (IT) refers to the computer systems, software applications, and networks used by medical professionals and healthcare facilities. It plays a big role in healthcare transformation. Key examples include Electronic Health Records (EHRs), which digitally store patient health history, and telemedicine platforms enabling remote video consultations with doctors.
These technological tools offer significant benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Digital systems allow staff to access patient records and information in seconds, eliminating the time spent searching through paper files. This efficiency means more time can be dedicated to direct patient care.
- Improved Accuracy and Safety: Computerized systems can include safeguards to help prevent errors. For instance, software can flag potential mistakes in medication dosages or alert doctors to possible drug interactions, enhancing patient safety.
- Facilitated Data Sharing: Secure systems allow different doctors or hospitals involved in a patient’s care to share relevant information quickly and securely (with appropriate patient consent). This promotes better-coordinated care and avoids unnecessary duplication of tests.
Behind these systems are software development companies that build the core tools and often AI development companies that integrate intelligent features. Their combined efforts lead to improved patient outcomes and smoother workflows for healthcare providers.
Key Components of Modern Healthcare IT
Several core technologies form the backbone of today’s digital healthcare environment:
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Digital versions of patients’ paper charts. EHRs consolidate patient information like medical history and diagnoses into one digital file. This centralized data provides clinicians with a comprehensive view of a patient’s health.
- Telemedicine Platforms: These technologies enable remote healthcare delivery through video conferencing, remote monitoring, and digital communication tools. They offer convenient access to care, especially for routine follow-ups, minor conditions, or patients facing geographical barriers.
- Data Analytics Systems: These systems collect and analyze large volumes of anonymized health data to identify trends, patterns, and insights. Hospitals use analytics to improve treatment effectiveness, predict disease outbreaks, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall care quality.
- Medical Imaging Software: This includes systems like PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) used to store, retrieve, distribute, and display medical images such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Advanced software may incorporate AI to help radiologists detect potential anomalies more quickly.
- Billing and Revenue Cycle Management (RCM): Software solutions designed to manage the complex financial aspects of healthcare, including patient billing, insurance claim processing, payment tracking, and compliance with regulations. Efficient RCM is vital for the financial health of healthcare organizations.
- Patient Engagement Platforms: Web portals and mobile apps help patients take an active role in their own care. They are a big part of healthcare transformation. These tools often let patients book appointments, view test results, read their health records, send secure messages to doctors, and learn from helpful resources.
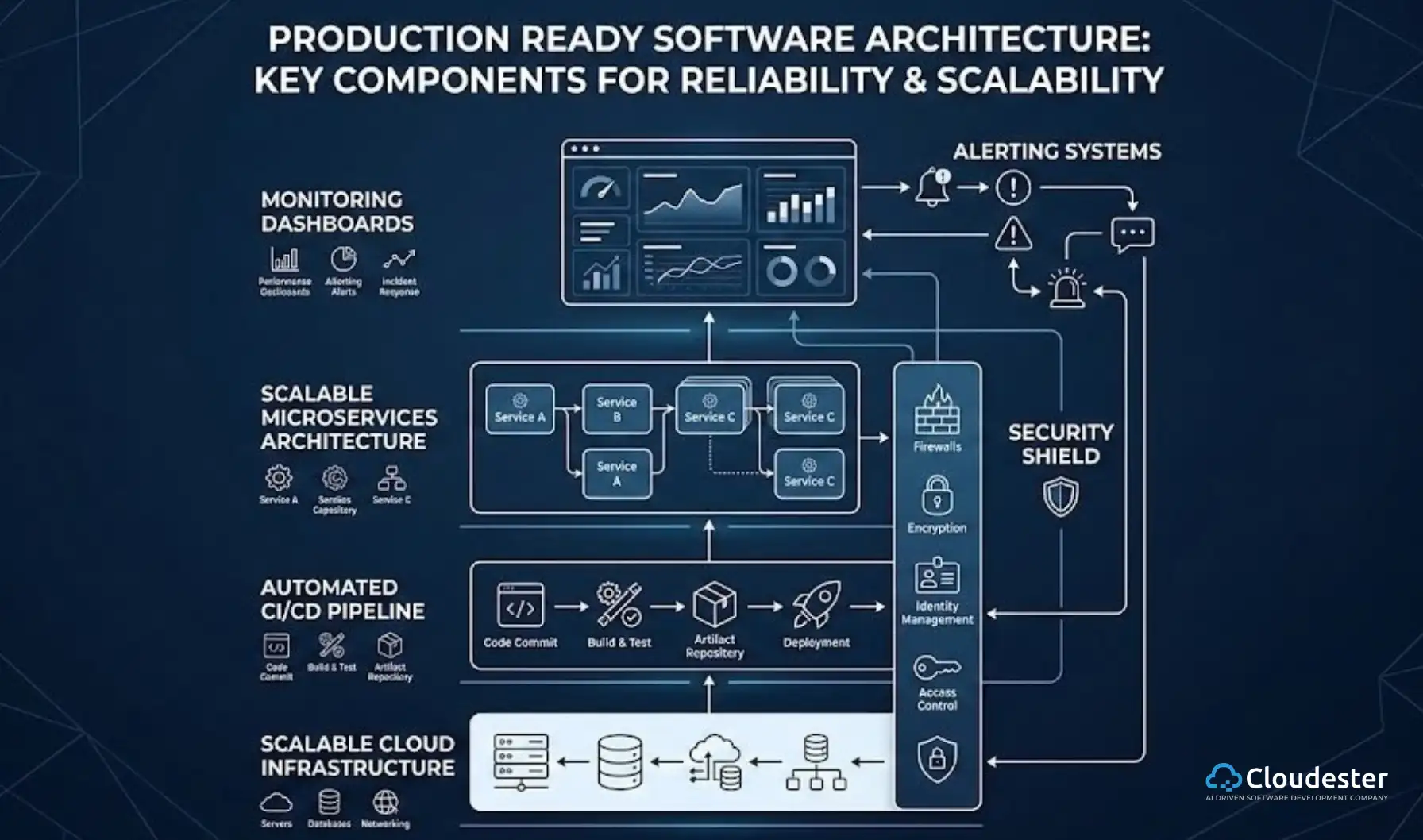
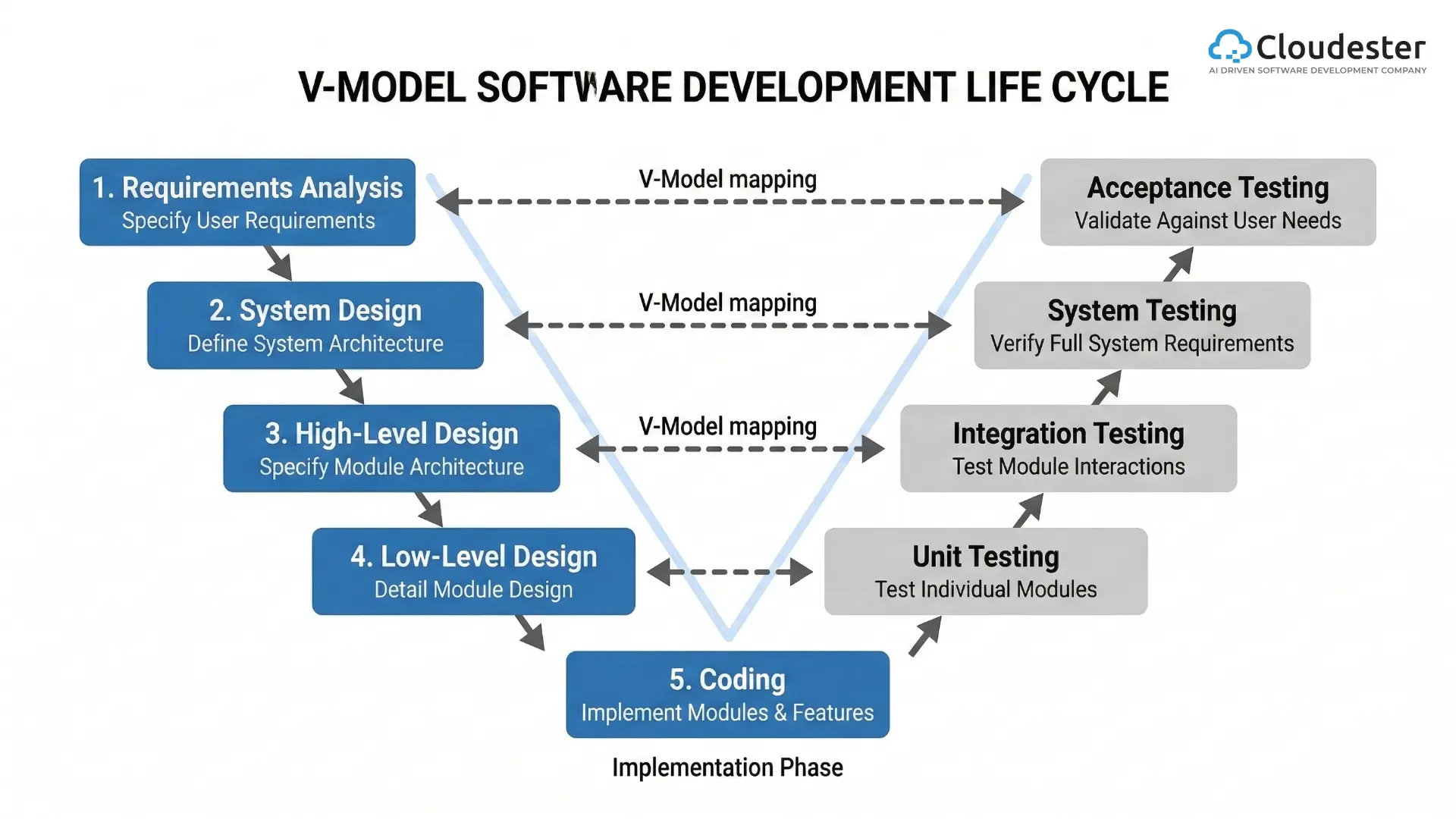
Robust software is essential for all these components. Integrating AI enhances their capabilities, enabling smarter, data-driven healthcare decisions.
The Role of Software Development Companies
Healthcare organizations have diverse needs; a small rural clinic operates differently from a large urban medical center. Software development companies specialize in creating customized solutions tailored to these specific requirements.
Their key contributions include:
- Ensuring Interoperability: They develop solutions that allow different IT systems (both old and new) within and between healthcare organizations to communicate and exchange data seamlessly. This prevents information silos and supports coordinated care.
- Implementing Robust Security: Protecting sensitive patient health information is paramount. Developers implement strong security measures, including data encryption, secure access controls (like multi-factor authentication), and compliance with privacy regulations like HIPAA.
- Focusing on Usability: Tools must be intuitive and easy for busy clinicians to use. Developers design user-friendly interfaces and workflows that integrate smoothly into clinical practice, minimizing disruption and maximizing efficiency.
Software companies tailor technology to fit users. This ensures IT systems effectively support, rather than hinder, care delivery.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
The Added Value of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI introduces capabilities that mimic human intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making, into healthcare technology.
Key AI applications include:
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms analyze patient data to identify individuals at higher risk for certain conditions or complications (e.g., hospital readmission, disease progression). This allows for proactive interventions and personalized care planning.
- Medical Image Analysis: AI can quickly study medical images and help radiologists spot possible problems. This supports healthcare transformation by finding signs of disease early, so doctors can take action sooner and improve patient care.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered conversational agents can handle routine inquiries, provide appointment reminders, help patients navigate healthcare services, and offer basic health information, freeing up human staff for more complex tasks.
AI serves as a powerful support tool for healthcare professionals, automating repetitive tasks and providing data-driven insights. It enhances clinical decision-making but does not replace the essential role of human expertise and empathy in patient care.
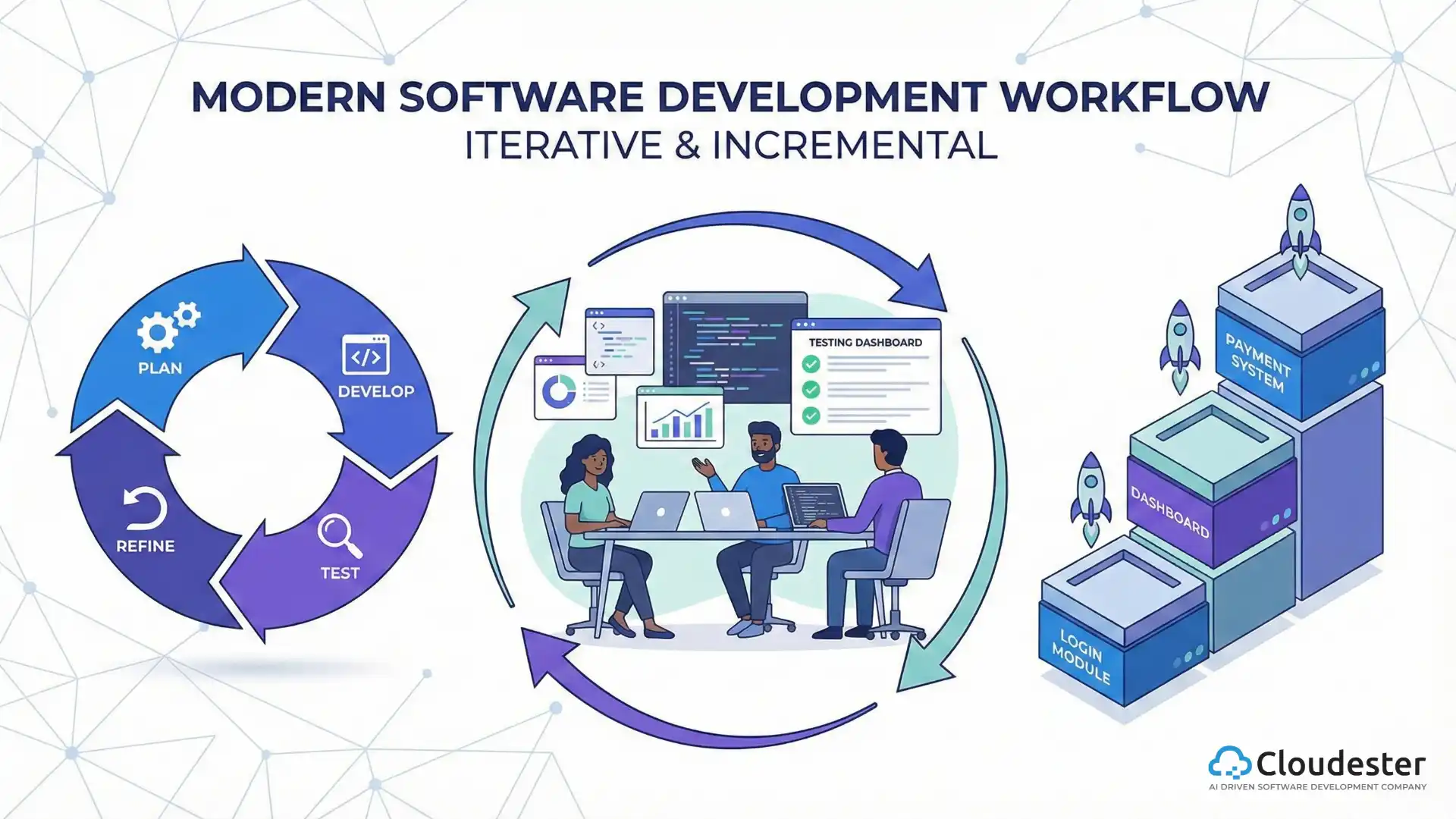
Synergy: When Software and AI Collaborate
The most significant advancements occur when software development and AI are integrated effectively. This synergy transforms standard tools into intelligent systems.
Consider these integrated examples:
- An EHR system enhanced with AI actively monitors patient data. It generates real-time alerts for clinicians about critical values or deterioration.
- A telemedicine platform with AI symptom checker gathers patient information. This makes virtual consultations with providers more focused and productive.
This collaboration creates healthcare systems that:
- Learn and Improve: AI models continuously refine their performance as they process more data (while maintaining privacy).
- Adapt to New Knowledge: Software allows for relatively quick updates to incorporate new medical guidelines or treatment protocols.
- Provide Real-Time Decision Support: Clinicians receive timely, relevant information and recommendations integrated directly into their workflow.
This teamwork accelerates progress towards earlier diagnoses, reduced errors, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and improved patient experiences.
Healthcare IT: Challenges and Opportunities
Implementing sophisticated technology in healthcare involves navigating certain challenges:
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to strict regulations like HIPAA, designed to protect patient privacy and data security, adds complexity to software development and deployment.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Healthcare data is a prime target for cyberattacks, requiring continuous investment in robust security infrastructure and practices to prevent breaches.
- Budget Constraints: The starting cost of using new IT systems in healthcare can be high. But with careful planning, these systems can support healthcare transformation and show long-term value or good returns.
However, these challenges are accompanied by significant opportunities:
- Expanding Telemedicine: Growing patient demand for virtual care drives innovation in creating more sophisticated, user-friendly, and integrated telemedicine solutions.
- Advancing Personalized Medicine: AI’s ability to analyze complex genetic, lifestyle, and clinical data holds immense potential for tailoring treatments to individual patients for better outcomes.
- Fostering Collaborative Innovation: Close partnerships between healthcare providers and technology developers ensure that new tools effectively address real-world clinical needs and challenges.
The Future Horizon of Healthcare IT
The evolution of healthcare IT promises further transformative changes:
- Predictive Health Monitoring: AI-driven systems may soon be able to reliably predict acute health events (like sepsis or heart failure) well before they occur, enabling preventative action.
- Seamless Data Interoperability: Secure, cloud-based networks will likely facilitate effortless and standardized data exchange across the entire healthcare ecosystem, providing a truly holistic view of patient health.
- Greater Patient Empowerment: Advanced wearables and mobile health apps will provide individuals with more detailed insights into their health status, encouraging proactive self-management and earlier detection of potential issues.
Intelligent software and AI are making healthcare more predictive, interconnected, and personalized, centering care on individual patient needs.
Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing the Right Technology Partner
The digital transformation of healthcare is well underway. To fully leverage its benefits, healthcare organizations need to collaborate with technology partners who possess the right expertise.
An ideal partner should:
- Understand Clinical Workflows: Deep knowledge of how healthcare professionals work is essential for building tools that are practical and enhance care delivery.
- Master Key Technologies: Proficiency in software development, AI, data analytics, and cloud computing is crucial for building scalable, reliable, and future-proof systems.
- Prioritize Security and Compliance: A steadfast commitment to data security and adherence to all relevant healthcare regulations is non-negotiable.
Organizations should work with experienced software and AI developers who understand the special needs of the healthcare world. This kind of teamwork supports healthcare transformation by helping them use the right technology. It leads to better care for patients and smoother daily operations. In the end, it helps create a healthier future for everyone.