AI Data Security Explained: Risks, Controls & Compliance

AI Generated. Credit: Google Gemini
Table of Contents
- What Is AI Data Security?
- Why Securing AI Data Is Critical Today
- How AI Data Security Differs From Traditional Data Security
- Key Risks in AI Data Protection
- Best Practices for Protecting AI Data
- Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
- How Enterprises Protect AI Data in Production
- Protecting AI Data in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
- AI Data Security vs AI Cybersecurity
- Common Mistakes Organizations Make
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Building Trust Through Secure AI Systems
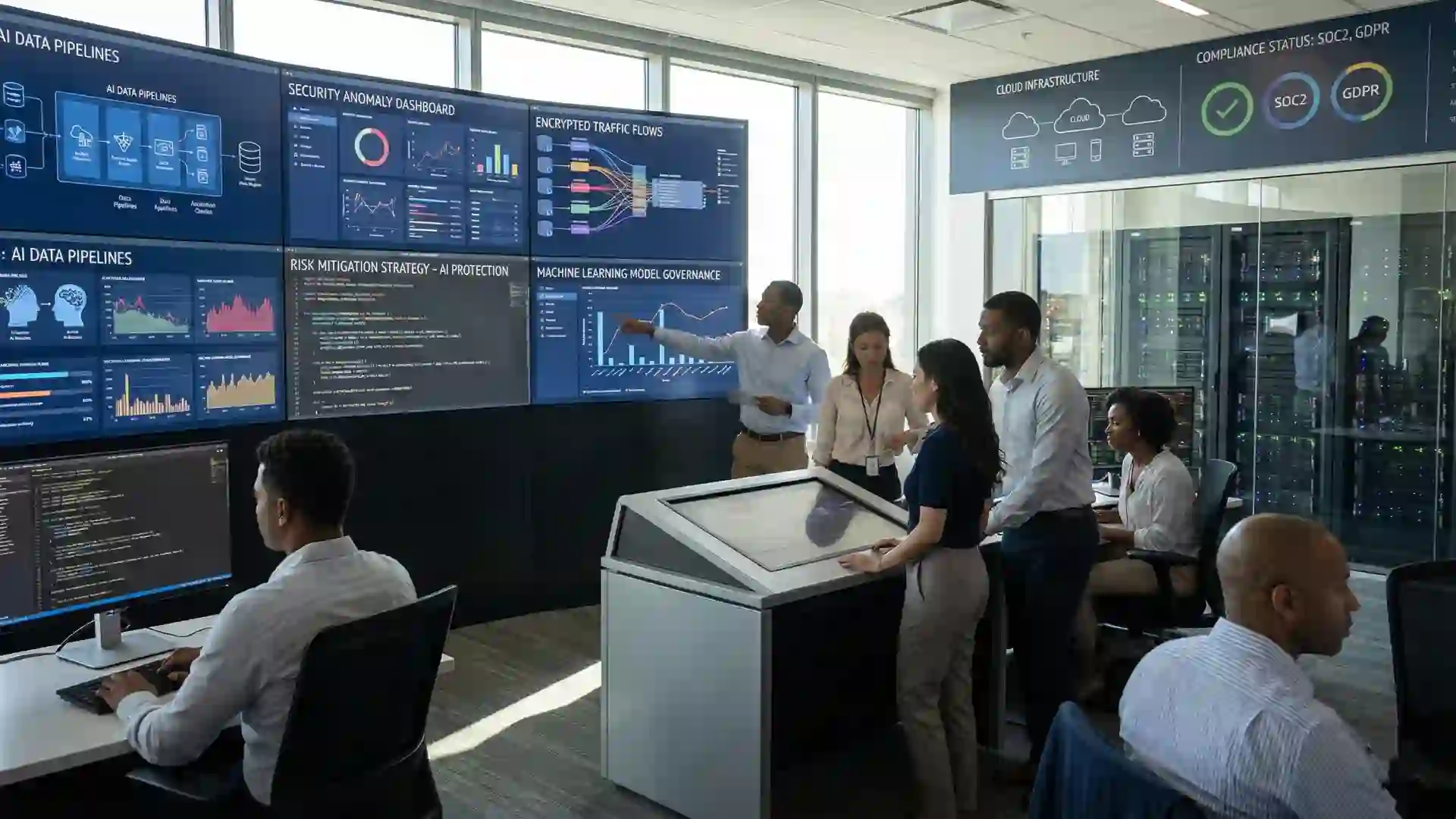
AI data security refers to the processes, technologies, and governance frameworks used to protect data throughout the artificial intelligence lifecycle, including data collection, model training, deployment, and inference. As organizations increasingly rely on AI systems to analyze sensitive information, protecting data used by AI models has become a critical requirement for maintaining trust, regulatory compliance, and operational integrity.
Unlike traditional approaches to data protection, AI-driven environments introduce new attack surfaces such as training datasets, machine learning models, and inference pipelines. Without strong safeguards, AI systems can expose confidential information, violate regulations, and damage organizational credibility.
What Is AI Data Security?
AI data security is the practice of safeguarding data used by artificial intelligence systems from unauthorized access, leakage, manipulation, or misuse across every stage of the AI lifecycle.
It focuses on protecting:
- Training datasets used to build machine learning models.
- Data stored within AI pipelines and feature repositories.
- Inputs and outputs during inference.
- Metadata, embeddings, and model artifacts.
Securing AI-related data is a core pillar of AI security strategy and directly supports broader data protection frameworks adopted by modern enterprises.
Why Securing AI Data Is Critical Today
The rapid adoption of artificial intelligence across industries has significantly increased the volume and sensitivity of data processed by intelligent systems. Modern AI applications frequently rely on personal, financial, healthcare, and proprietary business information, making them attractive targets for cyber threats.
Growing Use of Sensitive Information in AI Systems
Organizations now deploy AI to analyze:
- Customer identities, behavioral patterns, and preferences.
- Medical records, diagnostic images, and treatment data.
- Financial transactions and fraud detection signals.
- Intellectual property, trade secrets, and internal research.
As AI becomes embedded in core decision-making processes, failures in AI data governance can have enterprise-wide consequences.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
Emerging Threats Targeting AI Workflows
AI introduces security challenges that traditional data protection measures were not designed to address, including:
- Data poisoning attacks that compromise training datasets.
- Model inversion techniques used to infer sensitive data.
- Model extraction attacks targeting proprietary algorithms.
- Prompt-based exploits that expose inference-stage data.
These risks highlight the need to integrate AI risk management into existing cybersecurity programs.
How AI Data Security Differs From Traditional Data Security
Securing data for AI systems goes beyond encryption and access controls. It must consider how information influences model behavior and how trained models can unintentionally reveal sensitive data.
| Aspect | Traditional Data Security | AI Data Security |
|---|---|---|
| Data Lifecycle | Focuses on data storage and access | Covers training, inference, and retraining stages |
| Primary Assets | Databases and files | Training data, models, and prompts |
| Threat Surface | Data breaches and unauthorized access | Data poisoning, model extraction, inference leaks |
| Security Controls | Encryption and identity access management | Model governance, AI monitoring, secure pipelines |
Organizations implementing cloud security strategies must adapt them to address these AI-specific risks.
Key Risks in AI Data Protection
Understanding AI-related threats is essential for building effective defenses.
Training Data Leakage
Machine learning models can unintentionally memorize sensitive information from training datasets. Attackers may exploit this behavior to extract confidential records.
Data Poisoning Attacks
Malicious actors may inject corrupted or biased data into training pipelines, subtly altering model behavior without triggering conventional security alerts.
Model Inversion and Extraction
Attackers can reverse-engineer AI models to infer private training data or replicate proprietary model architectures.
Inference Data Exposure
Inputs and outputs during inference can leak sensitive information, especially in conversational systems and generative AI platforms.
Best Practices for Protecting AI Data
Organizations can reduce risk by implementing layered controls that combine technology, governance, and operational discipline.
Data Protection Controls
- Encrypt training, validation, and inference data at rest and in transit.
- Secure data pipelines using strict identity and access management.
- Apply anonymization and data minimization techniques.
Model Governance
- Restrict access to models based on least-privilege principles.
- Track model versions, datasets, and dependencies.
- Enforce approval workflows for deployment and updates.
Strong governance aligns with AI compliance requirements and enterprise security policies.
Secure AI Infrastructure
- Use isolated environments for training and experimentation.
- Protect inference APIs with authentication and rate limiting.
- Continuously monitor cloud configurations.
Monitoring and Auditing
- Log model activity and data access events.
- Detect anomalous behavior in real time.
- Conduct regular AI security assessments.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory compliance is a major driver of AI data protection strategies. Existing data protection laws often apply directly to AI systems.
Key Regulations Affecting AI Systems
- GDPR for personal data protection.
- HIPAA for healthcare-related AI applications.
- SOC 2 for enterprise trust frameworks.
- ISO 27001 for information security management.
Meeting these standards strengthens overall information security posture and reduces legal risk.
How Enterprises Protect AI Data in Production
Successful organizations follow structured processes to secure AI workloads at scale.
Step-by-Step Enterprise Approach
- Classify AI-related data based on sensitivity and regulatory impact.
- Apply encryption and identity controls across AI pipelines.
- Secure model training and evaluation environments.
- Monitor inference activity continuously.
- Audit compliance and refine controls regularly.
This approach integrates smoothly with enterprise AI governance models.
Protecting AI Data in Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Most AI systems operate in cloud or hybrid infrastructures, increasing complexity.
Key considerations include:
- Securing shared cloud resources.
- Protecting data movement across regions.
- Managing third-party AI services and APIs.
Organizations must align cloud computing security with AI-specific data protection measures.
AI Data Security vs AI Cybersecurity
AI data security focuses on protecting information used by AI systems, while AI cybersecurity addresses broader threats such as infrastructure attacks, AI-enabled malware, and platform vulnerabilities.
Both disciplines are essential components of a mature AI security architecture, but data protection remains the foundation.
Common Mistakes Organizations Make
Many security failures stem from underestimating AI-specific risks.
Common issues include:
- Using unverified public datasets for training.
- Exposing AI models through unsecured APIs.
- Ignoring inference-stage data leakage.
- Lacking formal governance for AI initiatives.
Avoiding these mistakes significantly strengthens AI trust and accountability.
Also read: The Role of Data Security in Custom IT Software Development
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is AI data protection different from cloud security?
Yes. Cloud security focuses on infrastructure, while protecting AI data addresses how information is consumed, transformed, and exposed within models.
2. Can AI systems leak sensitive information?
Yes. Without proper safeguards, models can unintentionally reveal training data or inference inputs.
3. How do organizations secure AI training datasets?
By encrypting data, restricting access, validating sources, and monitoring model behavior.
4. Which industries face the highest risk?
Healthcare, finance, government, and enterprises handling personal or proprietary data.
Building Trust Through Secure AI Systems
AI data security is no longer optional as organizations expand their use of artificial intelligence. Safeguarding data across the AI lifecycle reduces operational risk, supports regulatory compliance, and builds long-term trust in intelligent systems.
By combining governance, technical controls, and continuous monitoring, organizations can unlock the value of AI without compromising sensitive information.