Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC): Phases, Types, Test Cases, and Modern Tools
AI Generated. Credit: Google Gemini
Table of Contents
- What Is the Software Testing Life Cycle?
- Phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle
- Software Testing and Quality Assurance Explained
- Key Types of Testing Used in STLC
- Writing Effective Test Cases
- Understanding the Software Test Plan Structure
- API Testing Overview
- How AI Is Transforming Software Testing
- Career Path: Software Development Engineer in Test
- Benefits of Following a Structured Testing Life Cycle
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
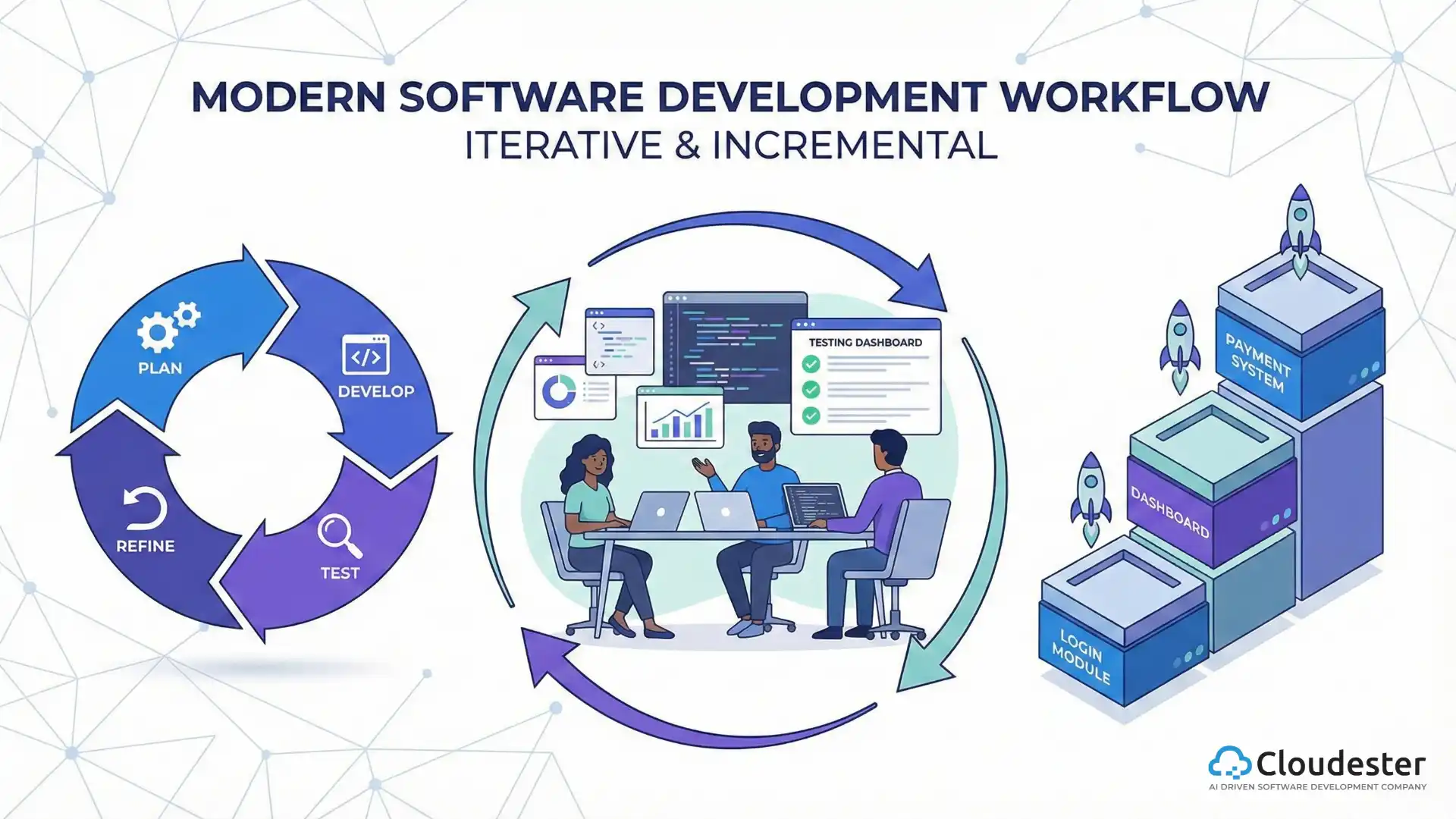
The software testing life cycle is a structured testing framework that ensures software applications meet quality, performance, and business requirements. It defines clear testing phases that help teams detect defects early, reduce development risks, and deliver reliable products.
Organizations that follow a defined STLC often align it with their broader software development services to ensure consistent quality across projects.
What Is the Software Testing Life Cycle?
The software testing life cycle (STLC) is a sequence of testing activities performed during the development process to validate functionality, usability, and reliability. Each phase has specific goals, deliverables, and exit criteria that guide the testing effort.
STLC works alongside software development life cycle models to ensure quality is maintained throughout development.
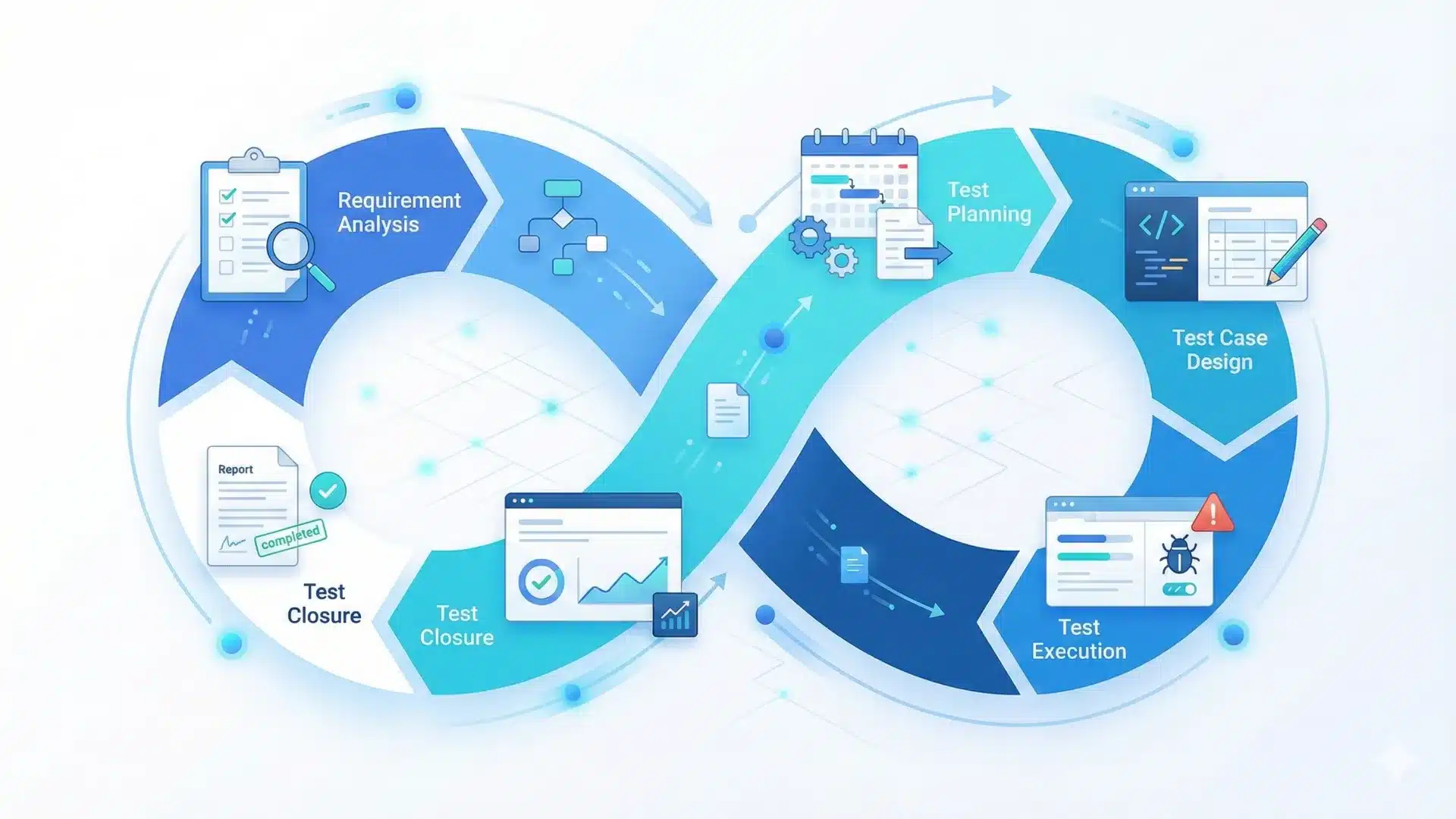
Phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle
The testing life cycle consists of six well-defined phases, each contributing to software quality.
Requirement Analysis
Testers analyze functional and non-functional requirements to identify testable features. Early involvement ensures clarity and reduces misinterpretation. This phase often overlaps with requirements analysis in software development.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
Test Planning
This phase defines the testing scope, objectives, timelines, tools, and risk mitigation strategy. A detailed plan ensures alignment with quality assurance strategies.
Test Case Development
Test scenarios, test cases, and test data are prepared based on approved requirements. These assets ensure consistent validation across builds and are often supported by test automation frameworks.
Test Environment Setup
A controlled environment is configured to match production settings. This helps ensure accurate and repeatable test results, especially in cloud-based testing environments.
Test Execution
Test cases are executed, and actual results are compared with expected outcomes. Defects are logged, tracked, and retested until closure using defect tracking tools.
Test Cycle Closure
Test metrics, defect trends, and improvement areas are documented to enhance future testing cycles and optimize software quality management.
Software Testing and Quality Assurance Explained
Many teams confuse software testing and quality assurance, but they serve different purposes.
| Software Testing | Quality Assurance |
|---|---|
| Focuses on identifying defects | Focuses on preventing defects |
| Product-oriented | Process-oriented |
| Reactive activity | Proactive activity |
| Performed after development | Applied throughout development |
Software testing focuses on identifying defects in the product, while quality assurance emphasizes improving processes to prevent defects. Together, they form the foundation of end-to-end QA services.
Key Types of Testing Used in STLC
Different testing methods are applied at various stages to ensure complete validation.
Sanity Testing
Sanity testing in software testing is performed after minor changes or bug fixes. It ensures that core functionalities work as expected before deeper testing begins, often as part of regression testing practices.
User Acceptance Testing
User acceptance testing validates business requirements and confirms that the software is ready for real-world use by end users. This phase is critical in enterprise software testing projects.
Writing Effective Test Cases
Well-structured test cases improve coverage and reduce execution time. Test cases in software testing describe steps, conditions, and expected results to validate application behavior.
Best Practices for Test Case Creation
- Understand requirements thoroughly.
- Write clear and concise steps.
- Define measurable expected outcomes.
- Review and update test cases regularly.
Teams often reuse detailed test cases in manual and automated testing workflows.
Understanding the Software Test Plan Structure
A test plan defines how teams conduct testing activities. A standard software test plan template includes objectives, scope, testing approach, resources, schedules, and risk management.
Test plans play a key role in aligning testing with project management methodologies.
API Testing Overview
API in software testing focuses on validating backend logic, integrations, and data exchange between systems. It ensures that services function correctly without relying on the user interface.
API testing is especially important in microservices architecture testing and modern application development.
How AI Is Transforming Software Testing
The adoption of AI in software testing is improving efficiency and accuracy across test cycles. AI-powered tools analyze historical data, identify defect patterns, and optimize test execution.
Teams now commonly use AI-driven approaches in test automation services to reduce repetitive manual effort.
Career Path: Software Development Engineer in Test
Understanding the software development engineer in test meaning helps professionals plan advanced testing careers. An SDET combines development expertise with automation and testing knowledge.
Core Skills for an SDET
- Programming and scripting
- Automation frameworks
- Test architecture design
- Analytical problem-solving
Many SDETs grow into roles within software quality engineering teams.
Benefits of Following a Structured Testing Life Cycle
Adopting a structured testing approach delivers measurable benefits:
- Early defect identification
- Reduced cost of fixes
- Improved software reliability
- Faster release cycles
- Better user satisfaction
These benefits directly support scalable software product development.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main goal of the software testing life cycle?
The primary goal is to ensure software quality by identifying defects early and validating functionality against requirements.
2. How does STLC differ from SDLC?
STLC focuses on testing activities, while SDLC covers the entire development process from planning to deployment.
3. Is manual testing still relevant?
Yes, manual testing remains essential for usability, exploratory, and user-focused validation, especially alongside automated testing solutions.
4. Can AI fully replace testers?
AI enhances testing efficiency but cannot replace human judgment and creativity.
5. What tools support modern testing practices?
Test management, automation, performance, and defect tracking tools support efficient testing workflows in enterprise QA environments.
Conclusion
The software testing life cycle provides a disciplined and repeatable approach to quality assurance. By combining structured testing phases, modern tools, and AI-driven techniques, organizations can deliver stable, secure, and high-performing software products.
A well-implemented STLC strengthens development efficiency and long-term business success through continuous quality improvement.