The future of Software Programming with Artificial Intelligence

AI Generated. Credit: OpenAI’s ChatGPT
Table of Contents
- Historical Context & Evolution
- Key Drivers Making AI + Software Programming Powerful Today
- Current Use Cases / Examples
- How AI Will Shape the Future of Software Programming
- Benefits & Opportunities
- Challenges, Risks & Ethical Considerations
- What Developers & Companies Should Do to Prepare
- Predictions / Vision for 2030
- Conclusion
Ever stared at a blank screen, knowing what you needed to build, but dreading the sheer volume of repetitive code? You’re not alone. Now, imagine if nearly half that code wrote itself. That dream is rapidly becoming reality: a stunning 41% of all new code is now being generated by Artificial Intelligence. This monumental shift is defining the new era of software programming with AI.
Software programming with artificial intelligence is the augmented craft where humans leverage large language models (LLMs) and machine learning tools to assist, accelerate, and automate critical steps across the development lifecycle.
Why does this topic matter today? The surge of sophisticated AI programming tools combined with the world’s insatiable demand for software is causing an irreversible industry disruption. The conversation about the future of programming has moved from whether AI will participate to how we master it.
This blog is your essential guide. You’ll learn how we got here, what tools are changing the game right now, how your role will evolve, and the ethical guardrails necessary for this revolution.
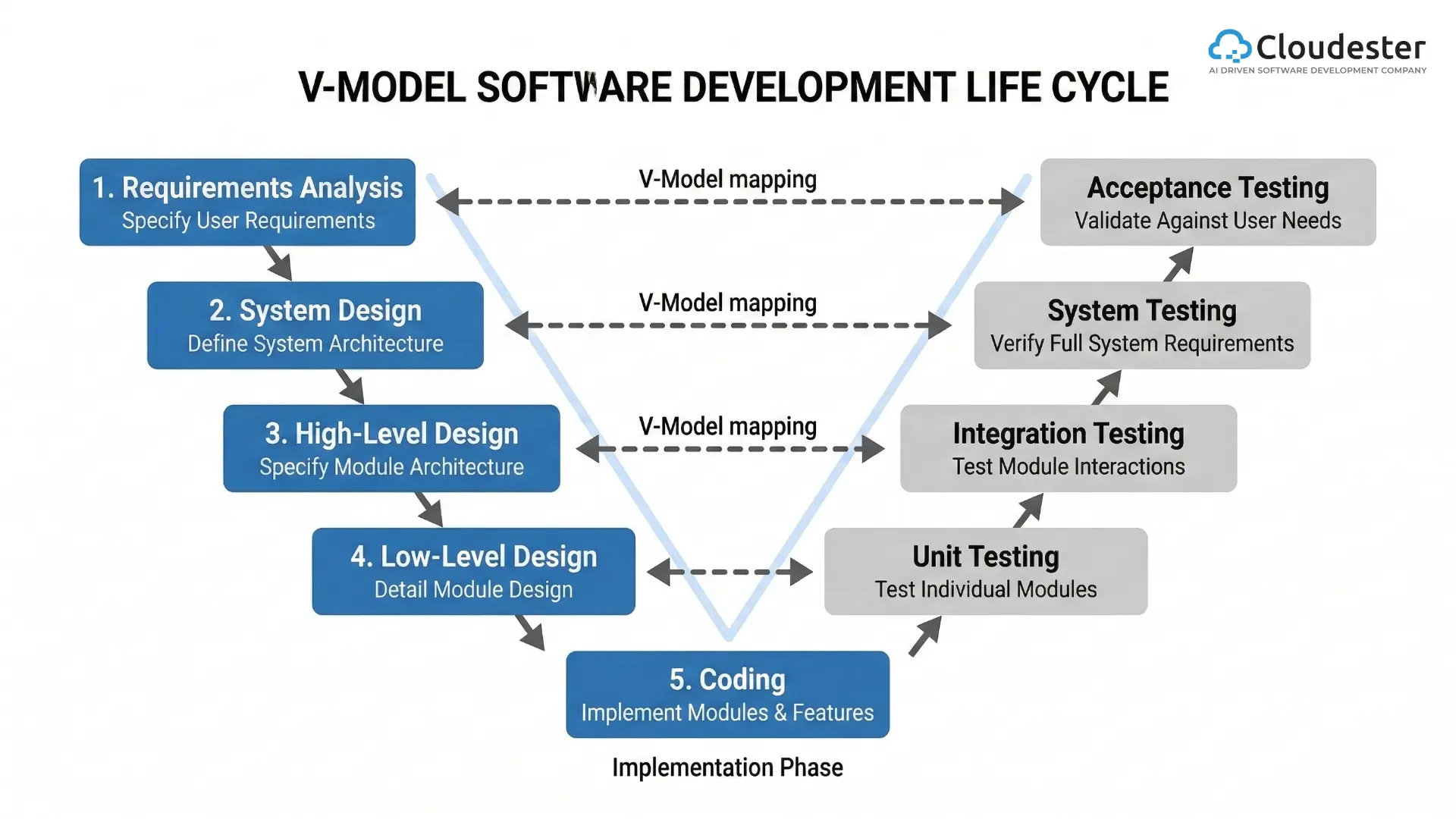
1. Historical Context & Evolution
Traditional software programming: strengths and limits
For decades, software development was a demanding, manual art. Its strength was the human mind’s ability to define complex systems, but it was slow and prone to human error. Development meant countless hours on boilerplate configuration, debugging, and repetitive tasks. Our output was capped by human speed and fallibility.
Early attempts at programming automation, code generation, and smarter IDEs
The industry always sought automation. Early Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) gave us basic autocompletion. Code generation tools built simple framework structures. While helpful, these were static, rule-based shortcuts. They lacked context and genuine intelligence.
The rise of AI/machine learning in developer workflows
The profound change began with true intelligence. When models based on machine learning for developers could analyze code and understand the intent behind a function, not just complete a word, the craft of software programming with AI was fundamentally redefined, ushering in the era of smart code assistance.
2. Key Drivers Making AI + Software Programming Powerful Today
The massive power of generative AI in coding stems from three perfectly converging technologies:
Advances in large language models (LLMs), embeddings, and transformers
The transformer architecture is central to this revolution. It enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to analyze code structure and semantics with human-like fluency. These models don’t just match patterns; they reason about context and logic.
Access to huge code/training datasets
AI learns from observation. Access to vast, public code repositories has trained these models to be polyglots, fluent in everything from Python to Go. This “education” makes modern AI programming tools immensely versatile.
Better compute infrastructure (GPUs, cloud)
Training and deploying these models requires serious computational muscle. Advances in GPUs and cloud infrastructure have made AI services economical and instantly deployable, integrating AI directly into your workflow.
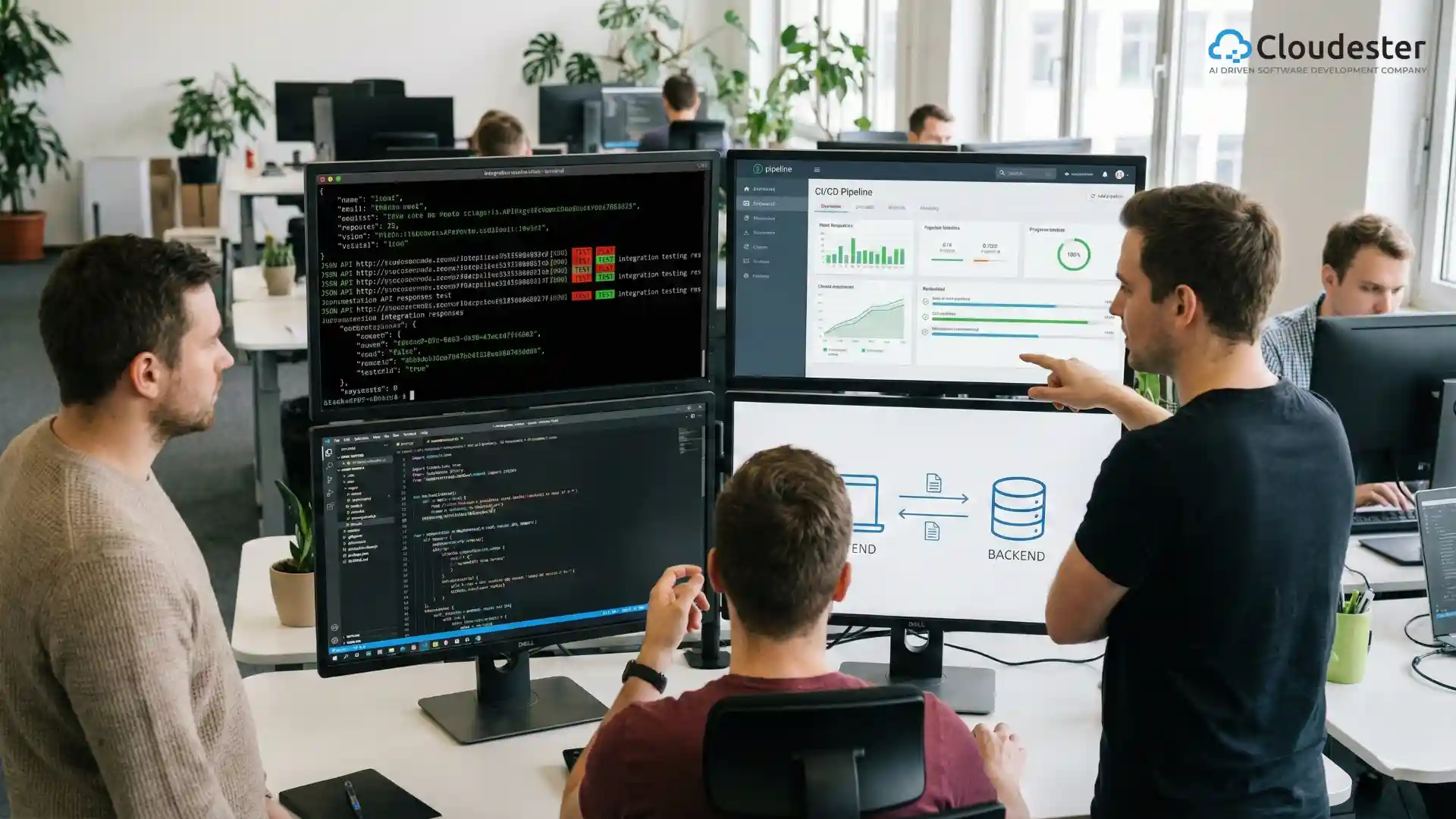
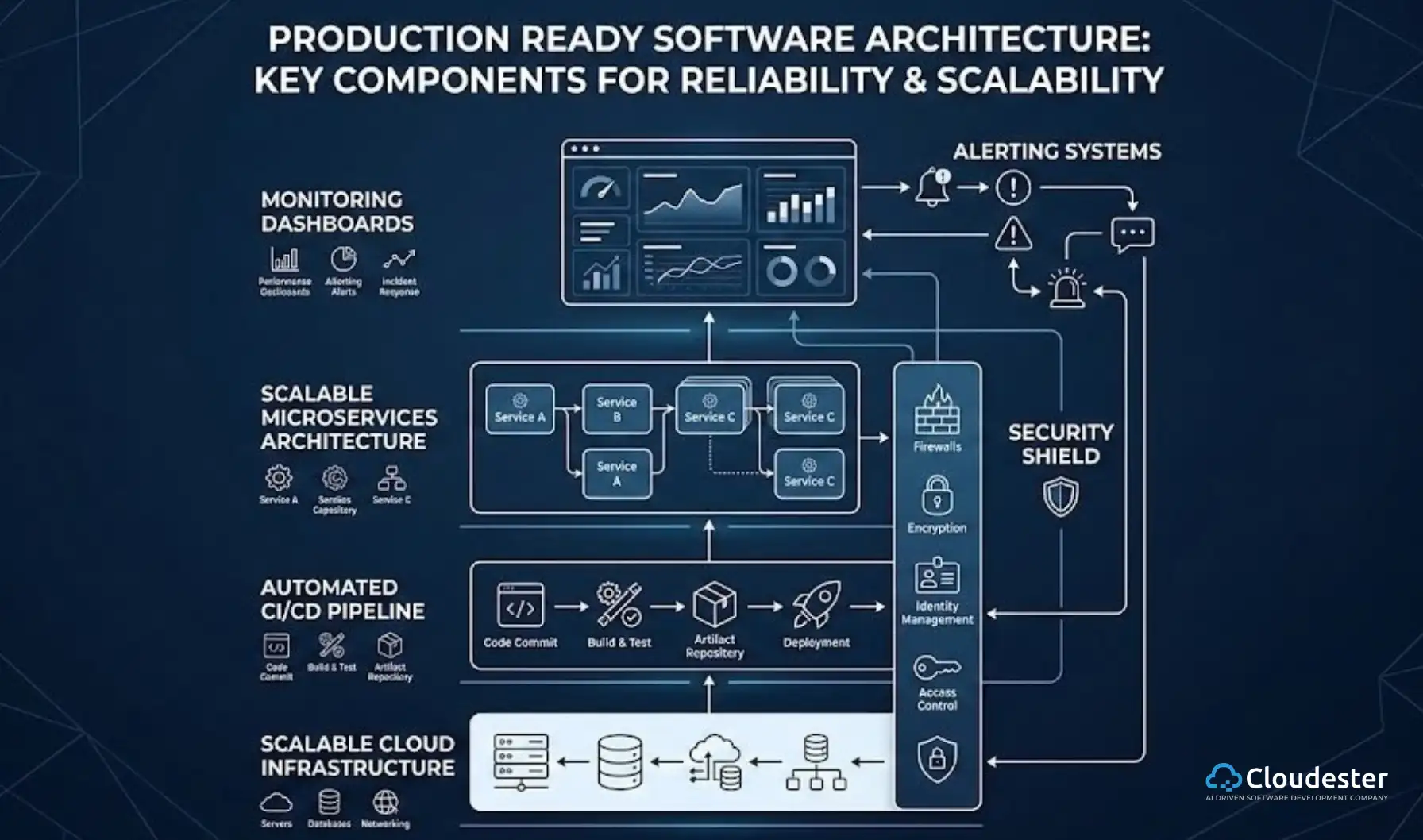
Tooling & integration (e.g., into IDEs, CI/CD pipelines)
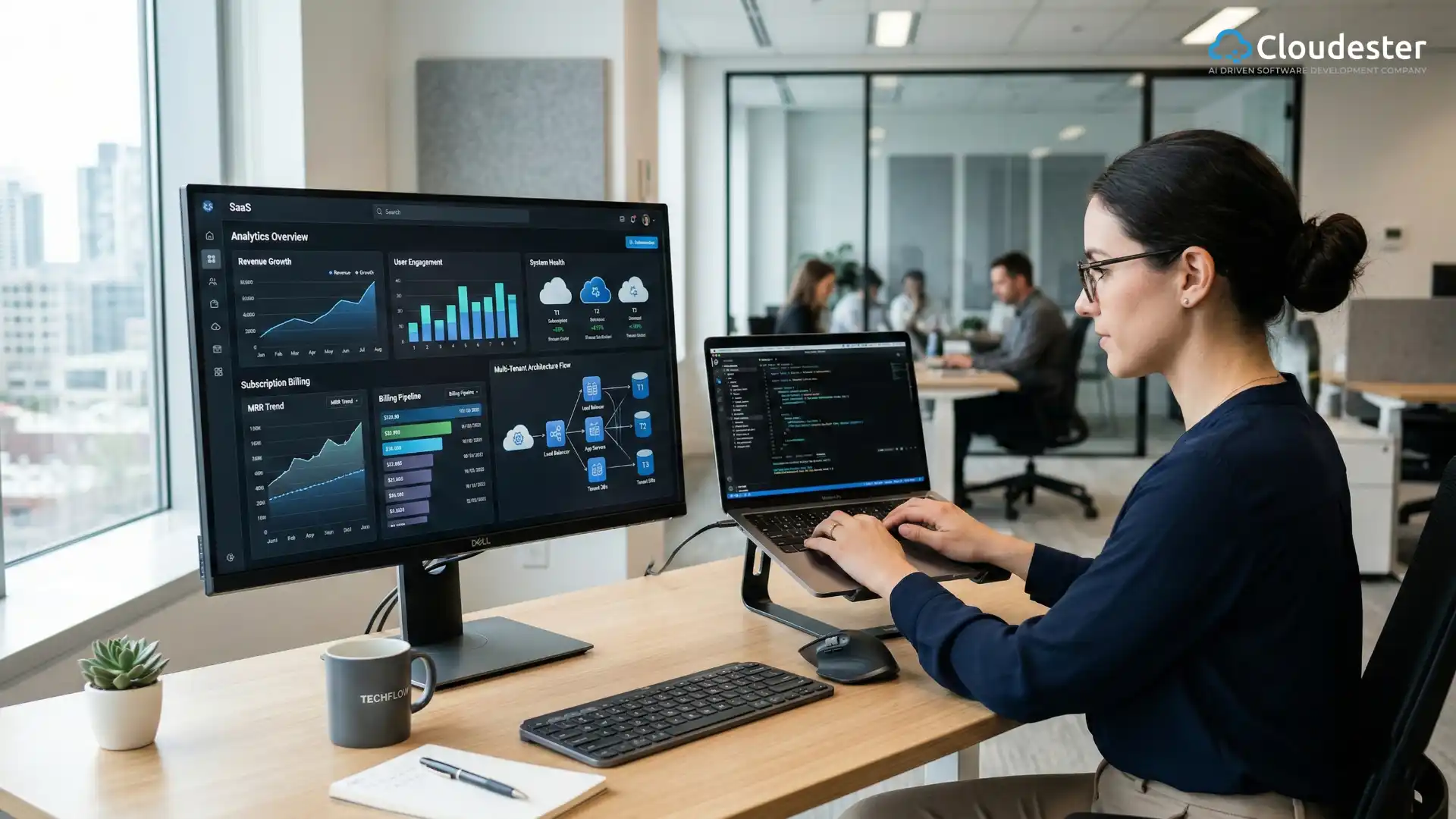
AI is now an embedded team member. Seamless integration into modern IDEs and CI/CD pipelines for automated security and testing is critical. Forward-thinking companies like Cloudester Software are rapidly integrating these platforms to enhance their service delivery speed and quality.
3. Current Use Cases / Examples
The landscape of software development with AI is already broad and incredibly useful:
AI code assistants (e.g. GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, etc.)
These tools are the frontline of AI code generation. They act as real-time pair programmers. Type a comment describing a function, and the AI drafts the code body, saving hours on boilerplate and context switching.
Automated code review, static analysis with AI
AI performs static analysis faster than humans, spotting subtle security flaws, performance bottlenecks, and style deviations before a commit is reviewed.
Generative UI / frontend code from design specs
Developers can provide a design mockup or a natural language description, and the AI generates the functional HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, dramatically accelerating frontend iteration.
Bug prediction & self-healing code
Advanced AI programming tools can analyze code changes and predict, with accuracy, which lines are most likely to introduce a bug, sometimes even suggesting or applying a fix automatically.
Test case generation / automated testing
AI can automatically spin up comprehensive unit tests that cover various edge cases based on the function’s implementation, drastically boosting code quality and saving QA time.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
4. How AI Will Shape the Future of Software Programming
By 2030, the programmer’s job will be fundamentally different, defining the future of programming.
Role shift: from writing manual code to overseeing AI-generated code
The core skill shifts from writing code line by line to critically reviewing and editing AI-generated code. Value will be in critical thinking, system design, and auditing, not code volume.
Agentic programming (AI agents that plan, write, debug)
We are moving toward autonomous AI agents. Developers will give an agent a high-level project goal (plan, code, test, and deploy), and the agent will manage the multi-step execution across the entire project.
New programming paradigms (conversational coding, prompt-driven)
Less time will be spent wrestling with syntax and more time talking to the editor. Prompt-driven development will become the primary interface, making clear communication a core technical skill in software programming with AI.
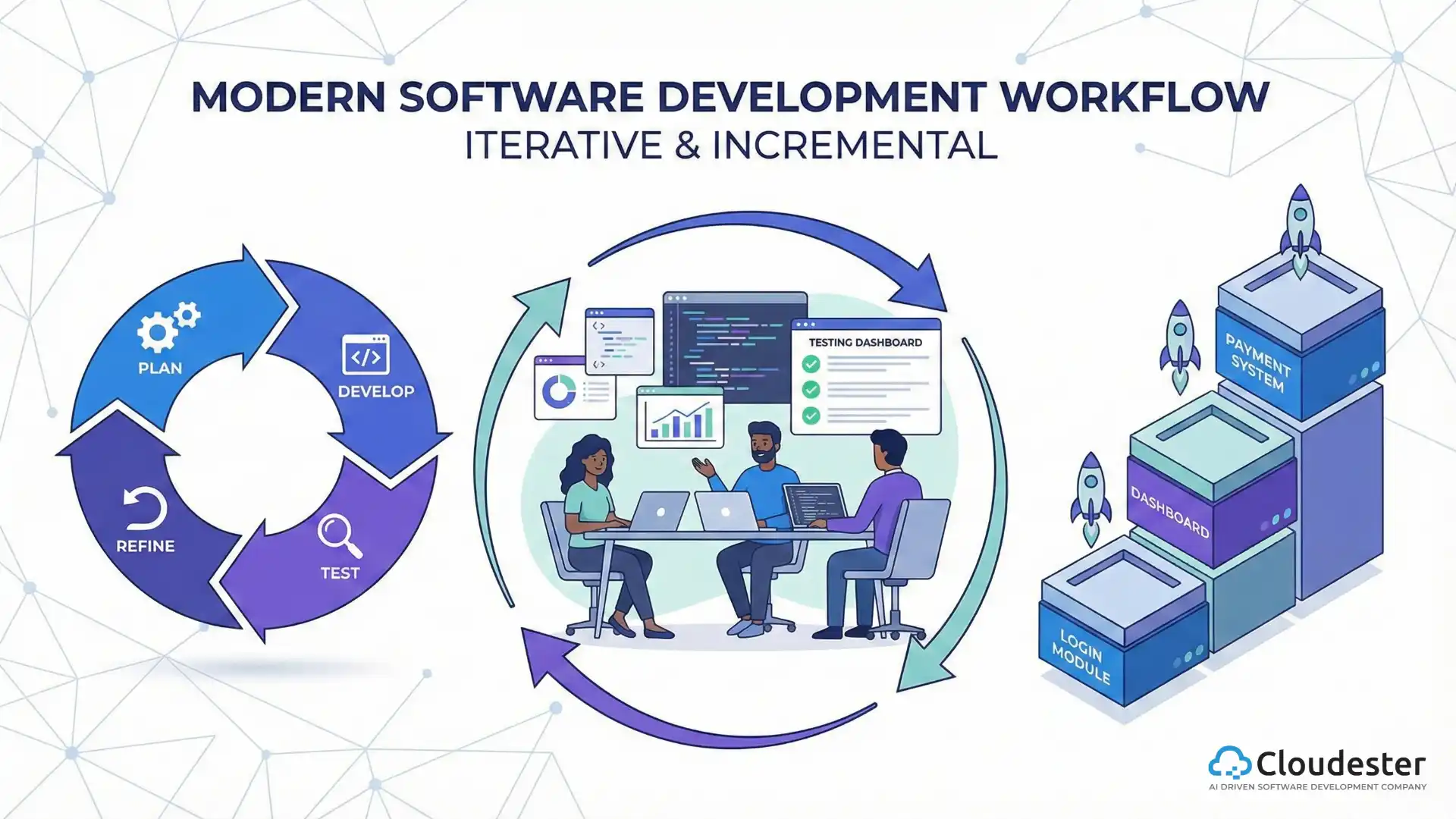
Hybrid human + AI collaborative workflows
Successful teams will master the hybrid human + AI collaborative workflow, where the machine handles the 80% and the human ensures the critical 20%, and the complex business logic and ethical constraints are sound.
Domain specialization (AI for different languages, niches)
We will see AI models that are highly specialized in specific domains like financial modeling or embedded systems programming, further refining the power of AI in software development.
5. Benefits & Opportunities
The benefits of fully integrated software programming with AI are transformative:
Increased productivity and speed allow faster delivery of high-quality software.
Lower barrier to entry for new developers is a major social benefit. Machine learning for developers handles syntax and boilerplate, allowing newcomers to focus on core logic and problem-solving.
Code consistency & standardization is a major win. AI produces highly consistent code, helping to reduce technical debt.
Enabling more experimentation & prototypes allows teams to quickly spin up proofs of concept without massive time investment.
Potential for more creative/high-level thinking is the ultimate promise. Developers are freed to tackle harder, more creative, strategic business problems. This allows companies, including our experts at Cloudester Software, to focus their human talent on high-value innovation.
6. Challenges, Risks & Ethical Considerations
This revolution demands caution. We must be honest about the risks:
Reliability, correctness, and debugging AI-generated code
AI code is not infallible. It can “hallucinate” plausible but buggy logic. Developers must retain the expertise to quickly debug and audit AI-generated code.
Bias, security & code vulnerabilities
If training data contains flawed patterns, the AI will reproduce them, potentially leading to security vulnerabilities or biases. Guardrails are non-negotiable.
Intellectual property, licensing of AI-generated code
Who owns the code generated by an AI trained on public, possibly licensed, codebases? This legal and ethical question of licensing and IP is still being debated.
Developer deskilling, job shifts, trust issues
There’s a real threat of developer deskilling. Teams must consciously foster foundational skills to prevent over-reliance on the AI safety net.
Maintaining codebase maintainability, readability
If developers rely too much on black box generation, codebases risk becoming a patchwork of styles, making long-term human maintenance and comprehension harder.
7. What Developers & Companies Should Do to Prepare
Adopt AI tooling gradually, pilot projects
Start small. Integrate one AI tool into a low-risk pilot project, establish clear metrics, and measure the real-world impact before scaling to critical systems.
Upskill in AI, prompt engineering, and model understanding
The new essential superpower is prompt engineering, learning how to clearly articulate complex, ambiguous requirements to the AI model. Understanding how AI models work is now critical.
Build guardrails: human review, testing, validation.
Always insist on human review and mandatory testing/validation for all AI-generated code, especially in critical areas.
Encourage hybrid workflows, feedback loops
Actively design workflows where humans and AI collaborate. Implement feedback loops so humans can correct AI outputs, helping the internal models improve over time.
Monitor AI advances, keep a flexible architecture.
The AI in software development landscape changes daily. Maintain a flexible, modular architecture that allows you to integrate new AI programming tools without a full system rehaul.
8. Predictions / Vision for 2030
By 2030, the title of “programmer” will likely evolve to Software Orchestrator or AI Architect.
What a “programmer’s day” might look like: The day will be spent validating system architecture, communicating business needs, auditing security reports from AI, and crafting sophisticated, multi-step prompts to steer autonomous development agents. Manual coding will be specialized.
Tools & ecosystems that may dominate will be natively AI-aware IDEs that provide cross-file context and function as a full “agent workspace.”
The boundaries (what AI might not replace) are the ability to grapple with ambiguity, creativity, and human-centric design. The problems we solve will shift from how to code something to what we should code and why it matters to the human end user.
Conclusion
The transformation underway in software programming with AI is not a threat; it’s an elevation of the role. It is an invitation to leave behind the tedious, manual grind and step into a future of programming focused on high-level design, creativity, and powerful collaboration—where capabilities like Embeddings as a Service enable smarter search, contextual understanding, and more intelligent applications. The era of the augmented developer is here.
Here’s your challenge: Open your favorite IDE, enable a code assistant, and commit to letting it write one full function or one full unit test entirely from your natural language prompt.
The biggest opportunity for developers is not learning how to write code faster, but learning how to lead the AI effectively. Go experiment today.