How Is Full Stack Web Development Changing with Cloud Computing?

AI Generated. Credit: Google Gemini
Table of Contents
- Defining the Terms
- How Cloud Computing is Shaping Full Stack Web Development
- What Skills Full Stack Developers Need in the Cloud Era
- Challenges & Considerations
- Case Studies or Real-World Examples
- Future Trends
- Conclusion
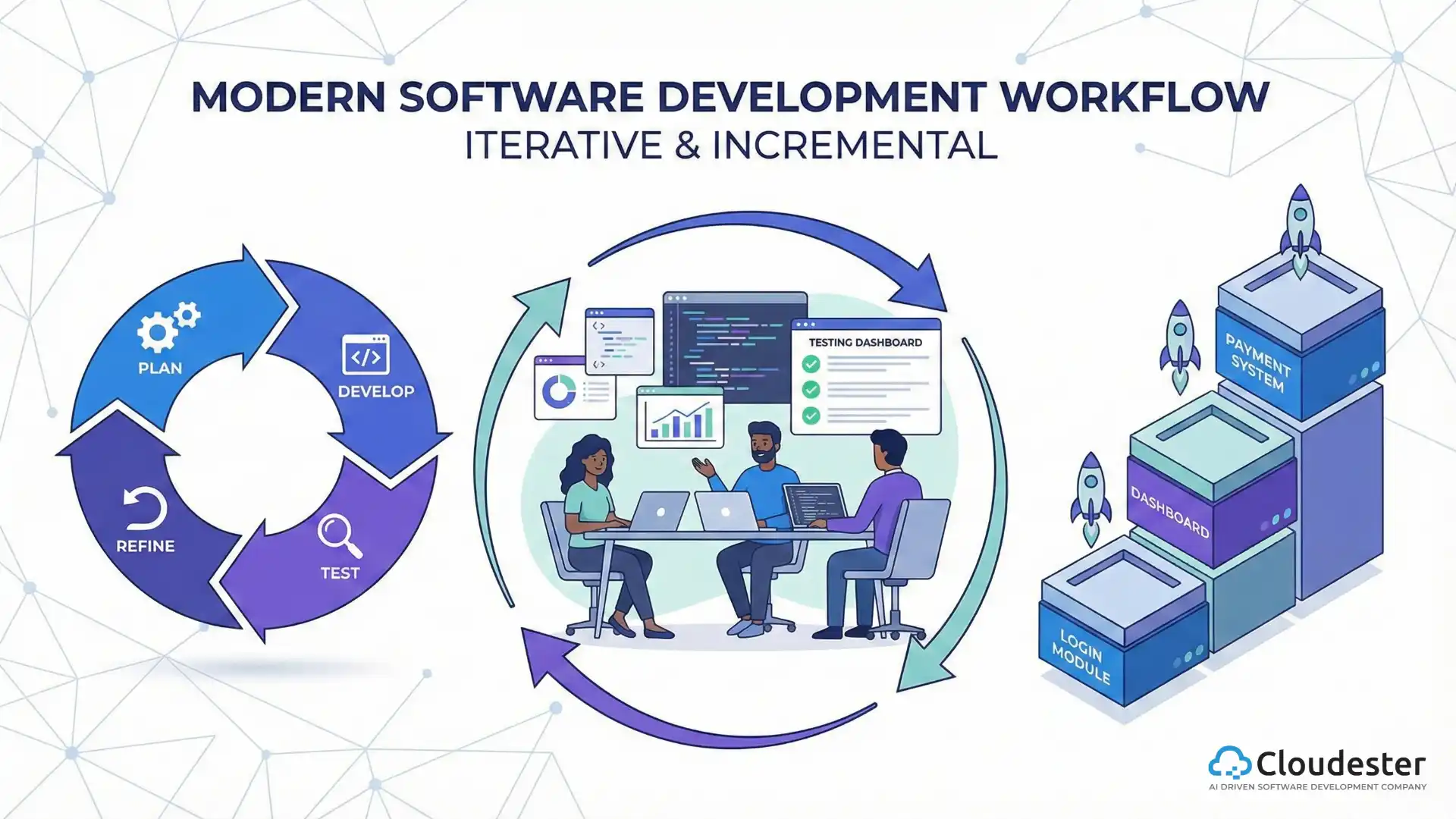
So, you’re a full-stack developer. You build everything from the buttons people click to the databases running the show. That’s full-stack web development! But here’s the big question: How does cloud computing change that job? The answer affects everyone building software. Before, you worried about physical servers, big computers in a room somewhere. The cloud is simple: it’s renting computer power, storage, and services over the internet. You don’t own the server; you just pay for the time you use it. Why is this a big deal? Because people expect apps to handle millions of users instantly. They want global access and new features today, not next month. The cloud makes this possible. We’ll look at the biggest shifts, the full-stack developer cloud skills you need, and where the industry is going next.
1. Defining the Terms
Let’s quickly review the basics.
What is a Full Stack Developer?
You’re the master builder. You can make an entire app, soup to nuts.
- Front-end: This is the visible stuff. The buttons, the layout, the user experience (using tools like React or Vue).
- Back-end: This is the hidden engine. The business rules, security, and talking to the databases.
You own the whole journey, from the user’s screen back to the data and back again.
What is Cloud Computing?
Think of the cloud like your electricity bill. You don’t build a power plant to run your lights; you just plug in and pay for what you use. Cloud companies (like AWS, Azure, and Google) offer power in three main flavors:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): Renting basic computer machines (Virtual Servers).
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): They give you a ready-to-go place to run your code. They handle the operating system and setup for you.
- FaaS (Serverless): This is the cool one. You run tiny pieces of code (functions) only when someone triggers them. You only pay for those split-second uses.
The cloud gives us huge scalability (it handles way more users), works everywhere, and saves money compared to old systems.
Custom AI Software Development Solution For Enterprises
2. How Cloud Computing is Shaping Full Stack Web Development
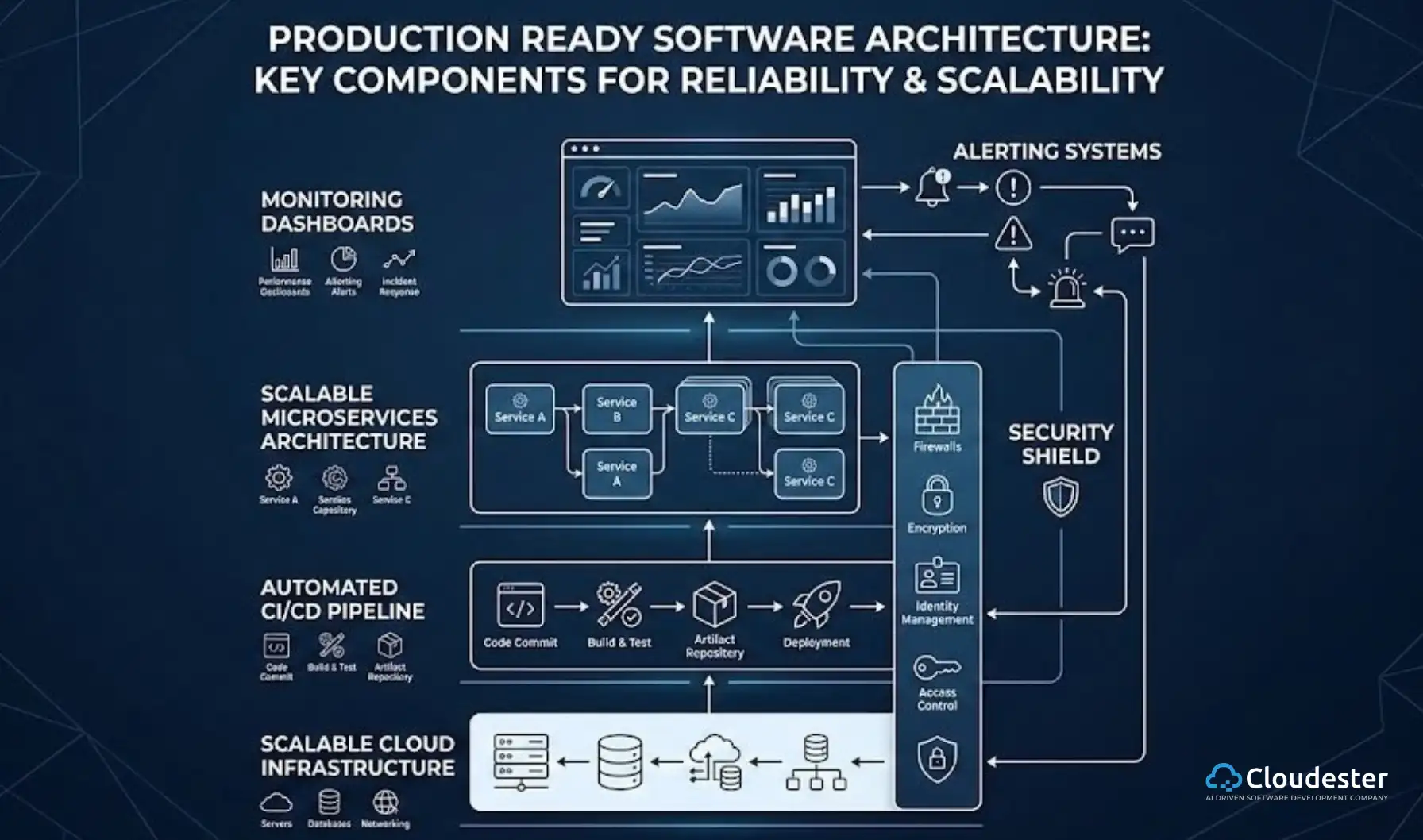
The biggest shift is this: your job changes from “fixing servers” to “managing smart services. “Deployment & Infrastructure. The most immediate change is that you don’t always have to manage the actual servers anymore. Cloud computing abstracts the infrastructure away. Old days meant spending hours setting up a virtual machine, line by painful line. Today, smart platforms handle that mess. Using PaaS (Platform as a Service) or Serverless platforms allows for lightning-fast deployment of full-stack web apps in the cloud. Tools like AWS Elastic Beanstalk, or services from Google Cloud or Azure, simply take your code, and they automatically set up the environment, handle the network, and manage the traffic. This move to managed services makes development much quicker.
Scalability & Performance
When you build a modern app, you have to assume you might get famous overnight. Traffic spikes and the need for global access require apps that can scale horizontally, meaning you add more small machines, not one bigger one. The cloud is the only environment that supports this dream instantly. It offers features like auto-scaling (instantly adding or removing computing power) and managed databases that grow automatically. This means your job is now about designing the app to handle this huge growth. You are building the kind of scalable web applications cloud environments demand, and you need to think not just about your code, but about how it runs in the cloud.
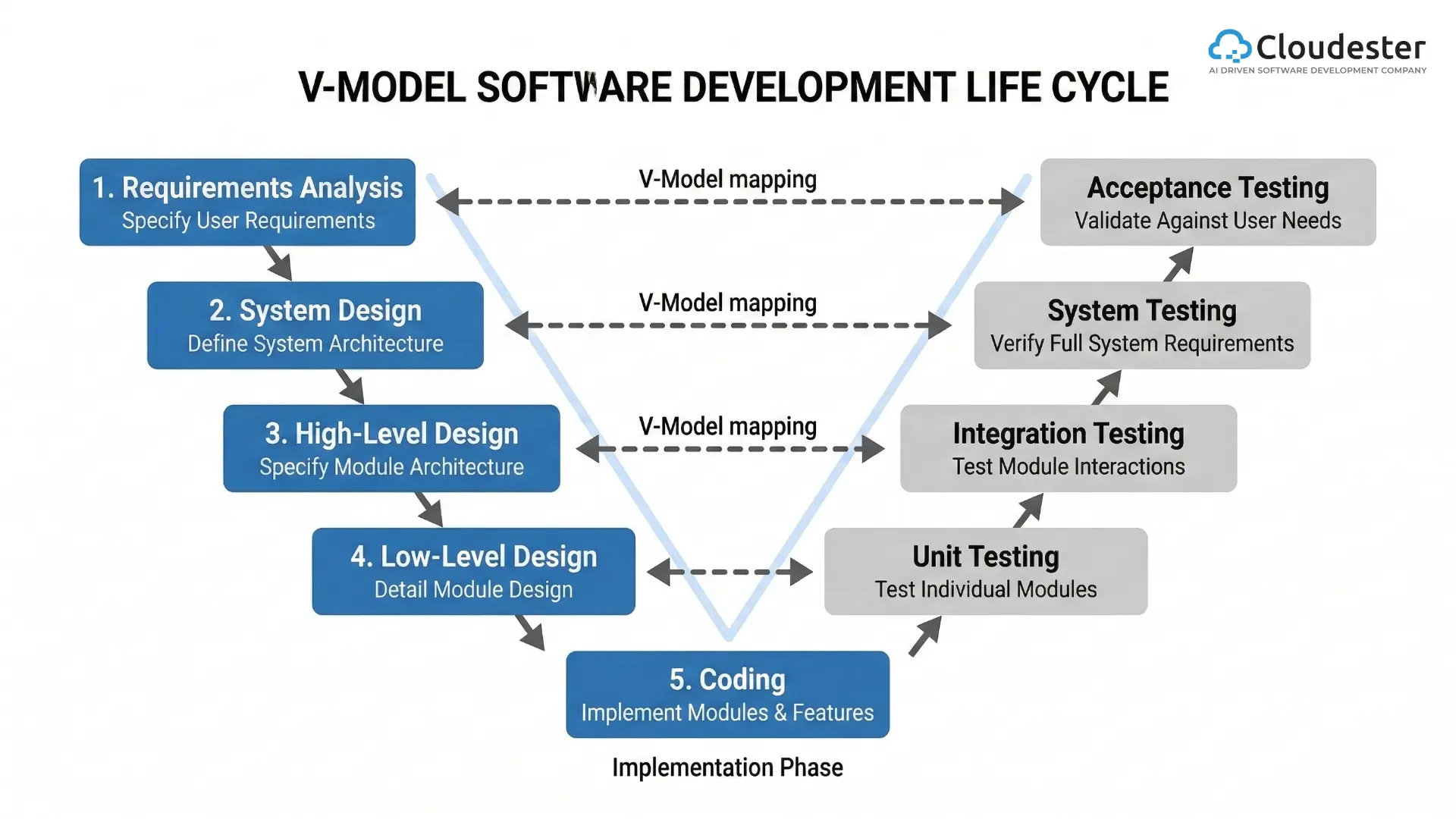
Development & DevOps / CI-CD Integration
The cloud has truly blurred the lines between Development (Dev) and Operations (Ops). Since you control cloud resources with software, you can automate the whole process of getting your app running.This is CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery). Today’s full-stack web development is tied to this pipeline. You, the developer, are often setting up the automated testing, building, and deployment sequence. You’re sharing duties that used to belong only to operations engineers, often taking on responsibilities for deployment and monitoring.
Cloud-Native Architecture & Modern Stacks
The design of modern cloud native full stack web applications is very different from those huge, single-block programs of the past. There’s a big shift towards:
- Microservices: You break the big program into many small, independent programs. You can update and scale each piece separately.
- Containerization: Tools like Docker wrap your code up neatly, guaranteeing it runs perfectly everywhere (often managed by Kubernetes).
- Serverless: The huge jump! You just write a small function (like checking a user’s password), and the cloud runs it only when needed.
The full stack is now evolving: it’s not just front + back, but the integration of infrastructure, services, and serverless functions. Companies like Cloudester Software focus on helping teams make this switch.
Cost, Collaboration & Global Reach
The “pay-as-you-go” cost model fundamentally changes how full-stack web development applications are built and maintained. If you leave a resource running that you don’t need, it’s wasting money. This makes cost awareness a core skill. The cloud also makes global teamwork easy. Teams all over the world can access the same development tools, share code, and deploy data globally. Because of this, understanding cloud costs and resource management is now part of the necessary full-stack developer cloud skills. So, what does this mean for your toolbox? You still need your core front-end and back-end skills, but you must add this cloud layer, which is part technical and part strategic.
3. What Skills Full Stack Developers Need in the Cloud Era
Technical Cloud Skills
You need a working knowledge of the tools that manage the cloud:
- Cloud Basics: You need fluent knowledge of core services from at least one big provider (AWS, Azure, or GCP).
- Container Skills: Know how to use Docker and understand how Kubernetes manages those containers.
- Serverless Building: The ability to design and deploy code using functions like Lambda.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): You must learn tools like Terraform. No more clicking buttons manually; you manage resources with code.
- Monitoring (Observability): Know how to use logging and tracking tools (like CloudWatch) to see if your connected apps are healthy.
Architecture and Strategy
Beyond the tools, you need to understand the strategy:
- Architectural Understanding: You need to grasp how microservices work, how to design for scalability, and how to build in security and cost optimization from the beginning.
Soft Skills
The shift to DevOps means collaboration is more important than ever. You need strong soft skills, including great communication and a true DevOps mindset, for working in distributed teams that share responsibility for the entire application life cycle.
4. Challenges & Considerations
The cloud is fantastic, but it has a few traps you need to watch out for.
- Security & Compliance: Managing security rules across dozens of small microservices is much tougher than securing one big server. You must also keep up with rules for compliance when running full-stack apps in the cloud across different countries.
- Cost-Control: If you don’t track resources, cloud costs can explode. Managing spending (or preventing Cost Sprawl) is a continuous job.
- Tool Fragmentation: The cloud ecosystem is massive. There are so many services that full-stack devs must pick and learn wisely, risking getting stuck with one provider or creating unnecessary complexity.
- Maintainability & Complexity: While microservices and serverless allow for massive scale, they introduce new challenges for debugging and testing. Building stable cloud native full stack web applications requires specialized knowledge because the system is made of so many small, moving parts.
5. Case Studies or Real-World Examples
To see how this works, let’s look at a financial app that tracks stock prices, a “before and after” scenario.
- Before Cloud (Traditional On-Premise Full Stack): A single, giant program ran on one computer server. If market traffic spiked during a news event, the server would crash. Someone had to manually fix it. This wasn’t a scalable web application cloud system at all.
- After Cloud (Cloud-Native Full Stack): The front-end is hosted globally for speed. The back-end is split into many tiny programs that run serverless on AWS Lambda. The database grows automatically. The entire setup is automated. If one piece breaks, the rest keep working, and the cloud handles millions of requests instantly. The app is deployed via an automated CI/CD pipeline, often using services on AWS/Azure/GCP.
This cloud-native shift makes the app truly resilient.
6. Future Trends
The future will be even simpler for developers, but also more complex in architecture.
- The Next Steps: We’ll see even more serverless options, extending to things like databases and containers. Edge computing (moving code closer to the user) will become standard to eliminate lag, and AI/ML integrated full-stack apps will be common, with developers calling AI features via cloud APIs instead of building them.
- How Roles Will Change: The full-stack web development job will keep moving away from fixing hardware and toward designing smart, flexible, automated systems. Your role may evolve into a “Cloud Architect-Lite” within the next 3-5 years.
- Advice for Teams: For developers and organizations, the message is clear: start adopting cloud skills today, rethink your architecture, and stay agile.
Also read: How Does a Software Development Company Work?
Conclusion
The cloud isn’t replacing full-stack web development, it’s completely transforming it. Your focus shifts dramatically:
- Deployment: Moving from manual server configuration to automated, managed service-based work.
- Architecture: Moving from single, monolithic programs to flexible, distributed microservices.
- Skills: Pivoting from deep operating system knowledge to broad architectural thinking and cloud developer skills.
The main takeaway is simple: mastering the cloud is not optional anymore. It’s the only way to build the highly scalable web applications that cloud environments demand. You need to evaluate your stack and skills, adopt cloud-native practices, and begin building truly cloud-ready full-stack applications.